Reflection, rotation and translation
Key Notes :
1. Reflection (Flip):
- Definition: A reflection is a mirror image of a shape or object across a line (called the line of reflection).
- How it works: Each point on the object is flipped to the opposite side of the line, maintaining the same distance from the line.
- Example: If you reflect a triangle across a vertical line, the triangle’s orientation changes as though it has been flipped over the line.
2. Rotation (Turn):
- Definition: A rotation is when a shape or object is turned around a fixed point (called the center of rotation).
- How it works: The shape rotates by a certain degree (e.g., 90°, 180°, or 270°) around the center point without changing its size or shape.
- Direction: Rotation can be clockwise or counterclockwise.
- Example: A square rotated 90° around its center point will still look like a square but will be turned to a new position.
3. Translation (Slide):
- Definition: A translation is when a shape or object is moved from one place to another without changing its size, shape, or orientation.
- How it works: All points of the shape move the same distance and in the same direction.
- Example: Moving a rectangle 4 units to the right and 2 units up is a translation.
4. Key Differences:
- Reflection: Creates a mirror image and changes the orientation.
- Rotation: Turns the shape around a point but keeps its orientation relative to the center point.
- Translation: Moves the shape without altering its orientation or size.
5. Symmetry:
- Reflectional Symmetry: If an object can be reflected across a line and still looks the same, it has reflectional symmetry.
- Rotational Symmetry: If an object can be rotated less than 360° and still looks the same, it has rotational symmetry.
Learn with an example
⛱️ What combination of transformations is shown below?
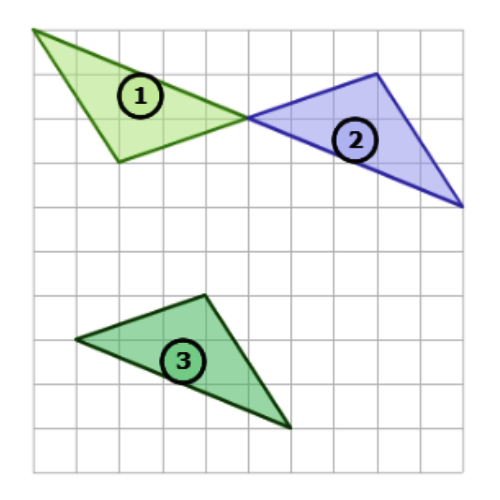
- translation, then rotation
- translation, then reflection
- rotation, then reflection
- rotation, then translation
- Use a rotation to turn Shape 1 into Shape 2. This image shows a rotation. Rotate the shape 180°.
- Use a translation to turn Shape 2 into Shape 3. This image shows a translation. Translate the shape down 5 and left 4.
- To go from Shape 1 to Shape 2 to Shape 3, use a rotation and then a translation.
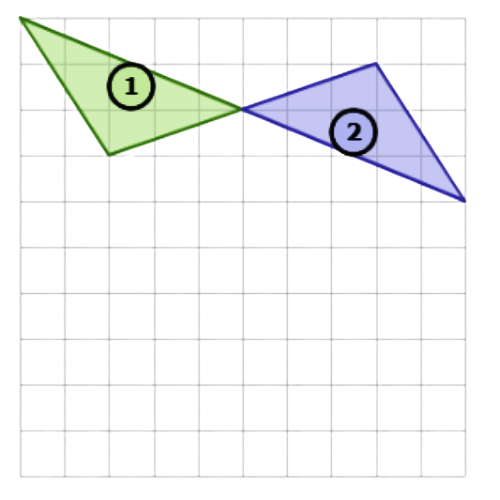
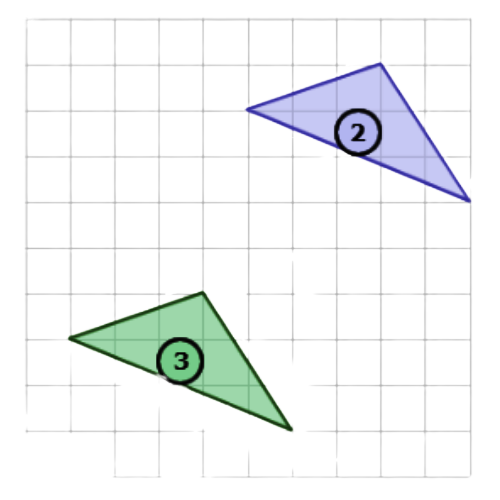
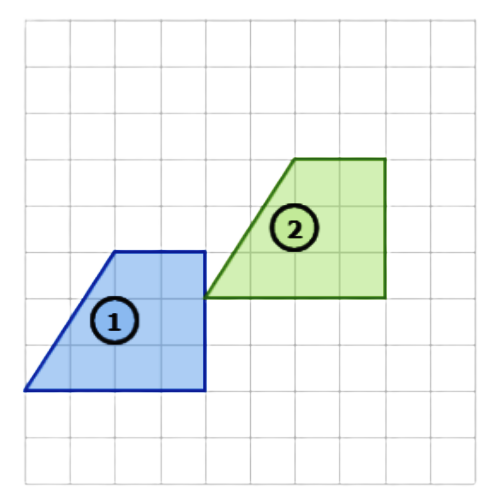
⛱️ What combination of transformations is shown below?
- rotation, then translation
- translation, then reflection
- translation, then rotation
- rotation, then reflection
- Use a translation to turn Shape 1 into Shape 2. This image shows a translation. Translate the shape up 2 and right 4.
- Use a rotation to turn Shape 2 into Shape 3. This image shows a rotation. Rotate the shape 180°.
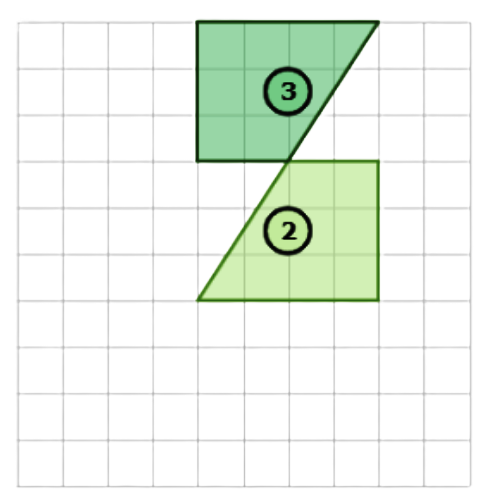
- To go from Shape 1 to Shape 2 to Shape 3, use a translation and then a rotation.
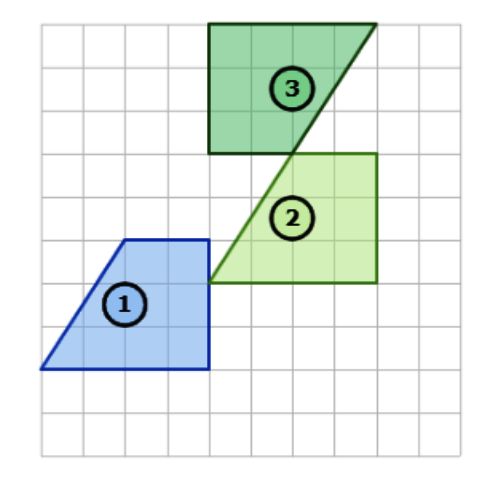
⛱️ What combination of transformations is shown below?
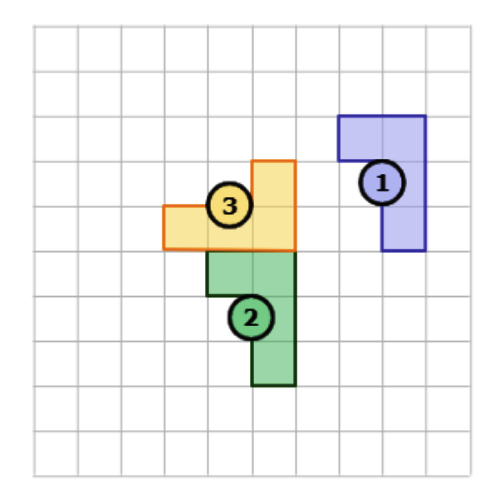
- reflection, then translation
- translation, then reflection
- reflection, then rotation
- translation, then rotation
- Use a translation to turn Shape 1 into Shape 2. This image shows a translation. Translate the shape down 3 and left 3.
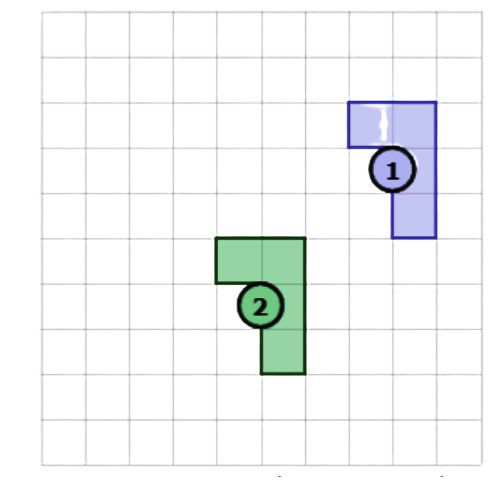
- Use a rotation to turn Shape 2 into Shape 3. This image shows a rotation. Rotate the shape 90° clockwise.
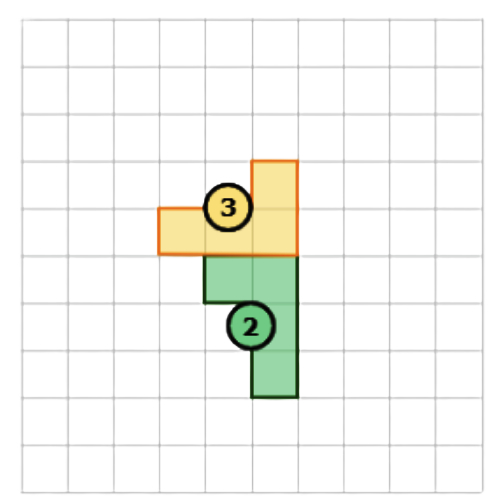
- To go from Shape 1 to Shape 2 to Shape 3, use a translation and then a rotation.
Let’s practice!🖊️

