Flower
flower by Delta publications
Key Notes :
Definition of a Flower
- A flower is the reproductive part of a plant that is often colorful and fragrant.
- It is responsible for producing seeds through the process of pollination and fertilization.

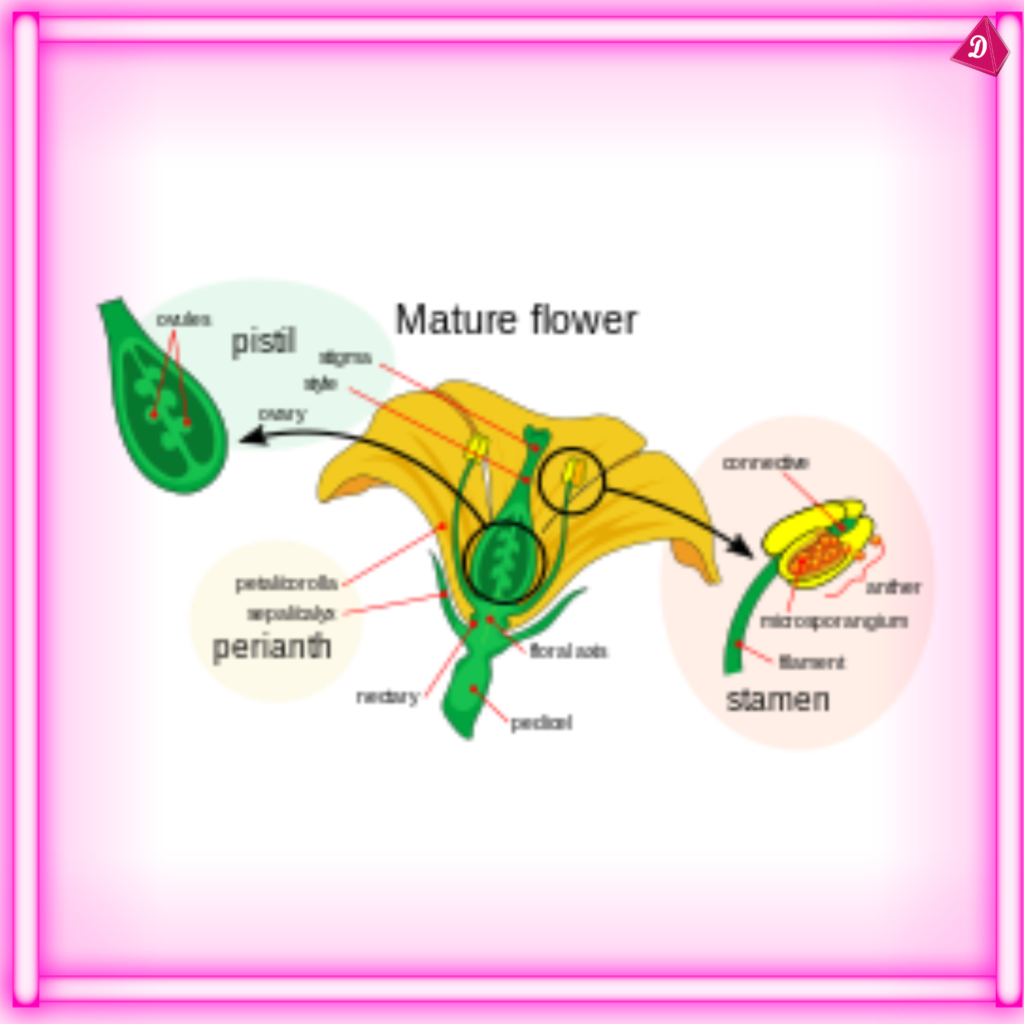
Parts of a Flower
- Sepals: The green, leaf-like parts at the base of the flower that protect the bud before it opens.

- Petals: The colorful parts of the flower that attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds.

- Stamen: The male reproductive part of the flower, consisting of the anther and filament. The anther produces pollen.
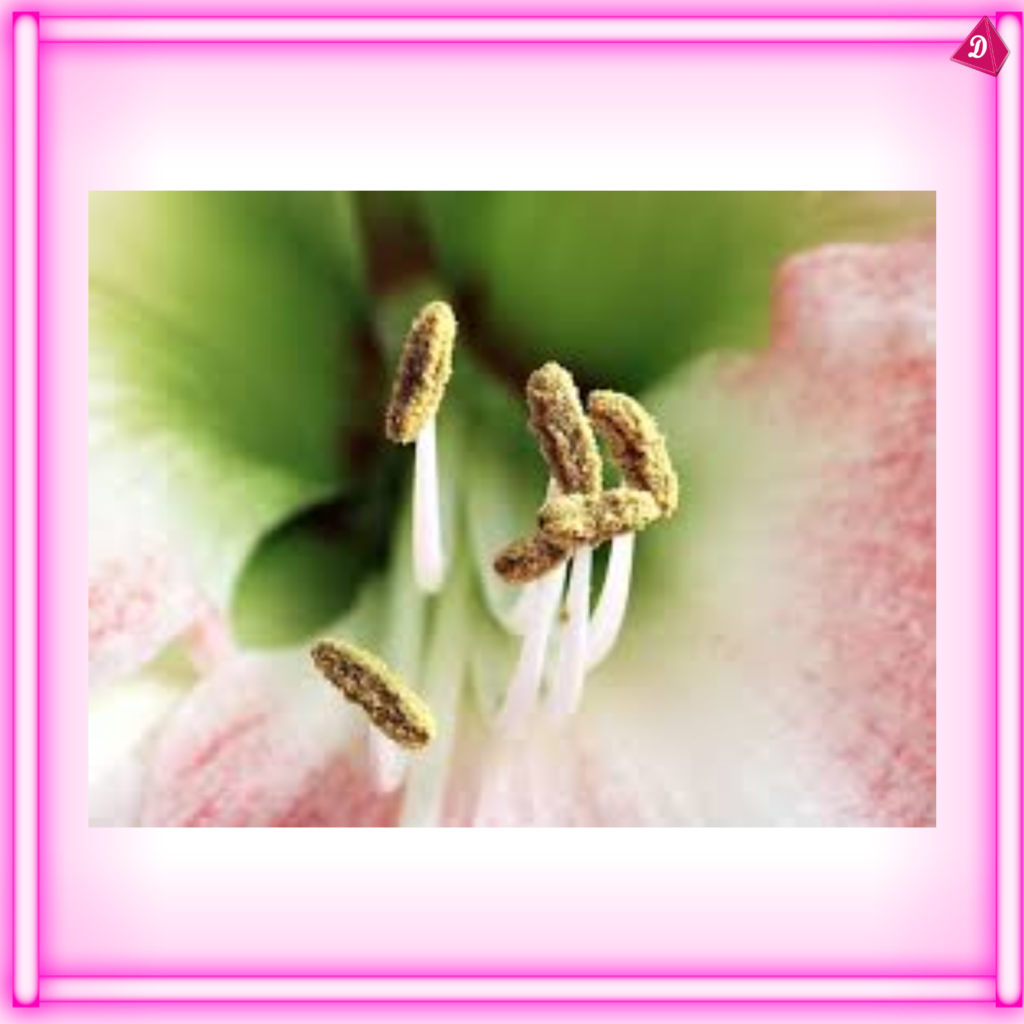

- Pistil (Carpel): The female reproductive part, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization.
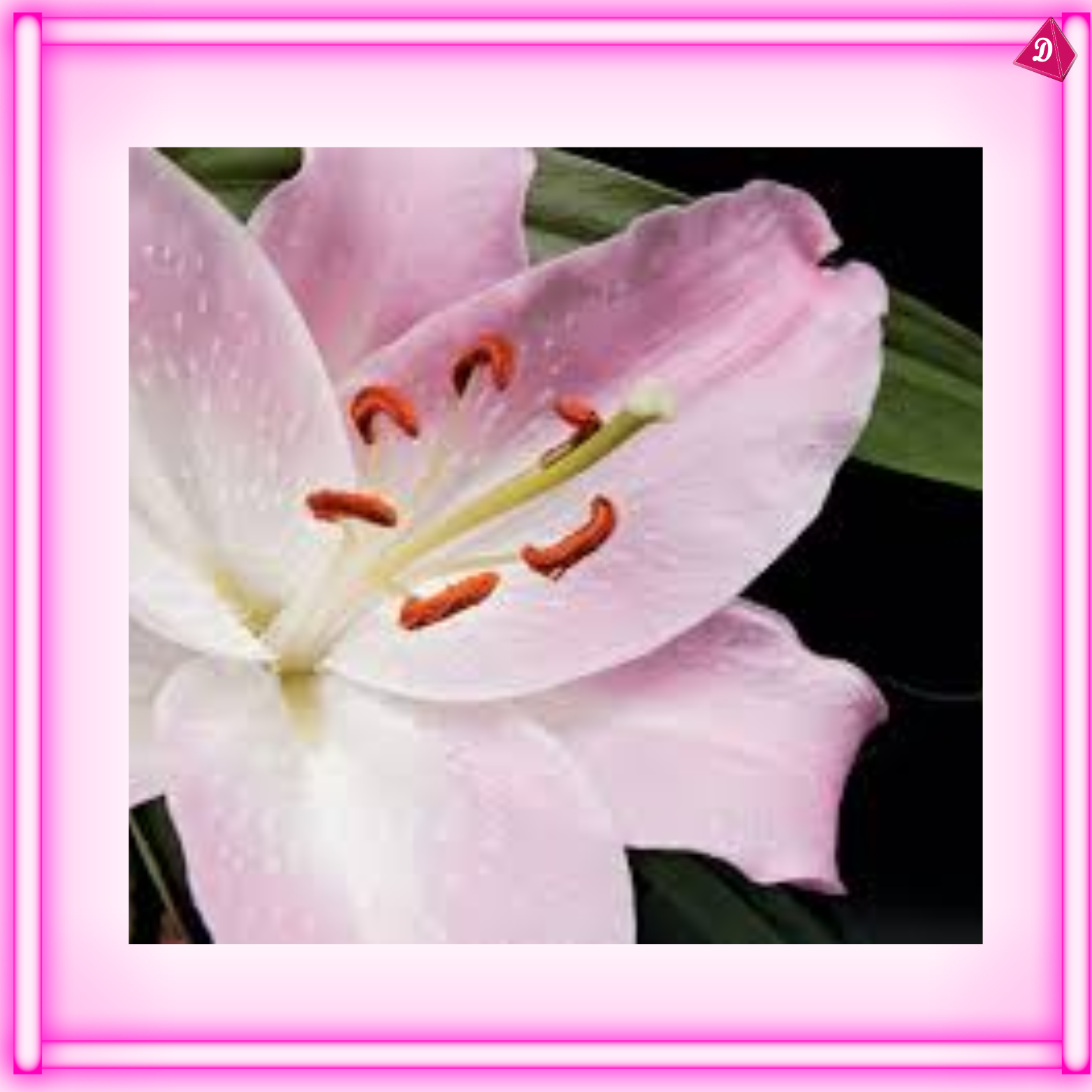

Pollination
- The process of transferring pollen from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of a flower.
- Pollination can be done by wind, water, animals (insects, birds), or by humans.

Fertilization
- After pollination, the pollen travels down the style to the ovary, where it fertilizes an ovule.
- The fertilized ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary becomes the fruit.
Types of Flowers
- Complete Flowers: Flowers that have all four main parts (sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils).
- Incomplete Flowers: Flowers that are missing one or more of the main parts.
- Bisexual (Perfect) Flowers: Flowers that have both male and female reproductive organs.
- Unisexual (Imperfect) Flowers: Flowers that have either male or female reproductive organs.
Importance of Flowers
- Flowers play a vital role in plant reproduction by enabling the production of seeds and fruits.
- They attract pollinators, which helps in the cross-pollination process, increasing genetic diversity.
- Many flowers are used for ornamental purposes, in perfumes, and as symbols in various cultures and traditions.
Examples of Common Flowers
- Roses, lilies, sunflowers, tulips, and daisies are examples of common flowers with diverse colors, shapes, and sizes.
Human Uses of Flowers
- Flowers are used in various industries, including floriculture, perfumes, and medicine.
- They are also important in cultural rituals, decorations, and as symbols of love, friendship, and mourning.
Adaptations of Flowers
- Flowers have adapted to their environment and pollinators. For example, bright colors attract insects, while nocturnal flowers might attract moths or bats.
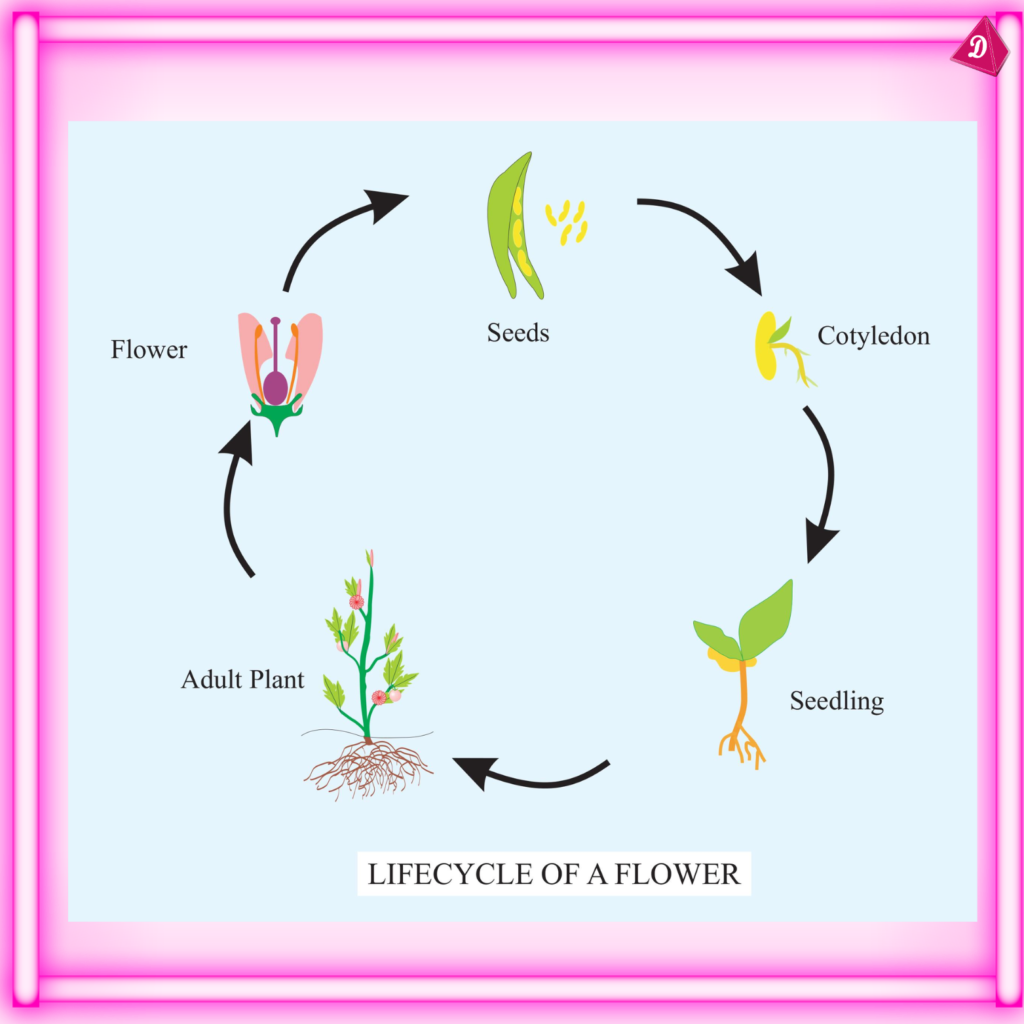
Life Cycle of a Flower
- The life cycle includes germination, growth, blooming, pollination, fertilization, seed formation, and dispersal.
Let’s practice!

