Root
root by Delta publications
Key Notes :
1. Introduction to Roots
- Definition: Roots are the underground part of a plant that anchor it in the soil and absorb water and nutrients.
- Importance: Roots are essential for the survival of the plant as they provide stability and nourishment.
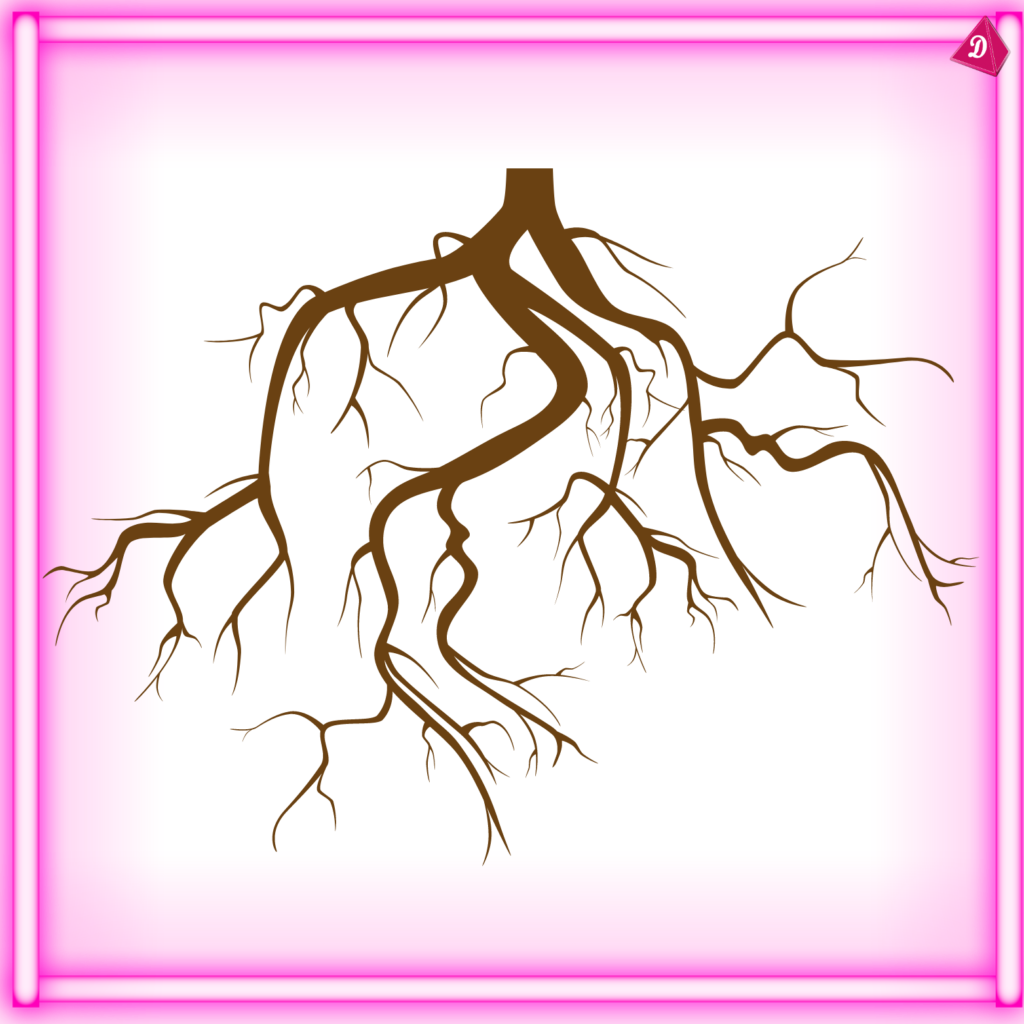

2. Types of Roots
- Taproot System:
- Features a main root that grows deep into the soil with smaller lateral roots branching off.
- Common in dicots (e.g., carrots, radishes).

- Fibrous Root System:
- Consists of many small roots that spread out in the soil, with no single dominant root.
- Common in monocots (e.g., grass, wheat).

3. Functions of Roots
- Absorption: Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil, which are essential for plant growth.
- Anchorage: Roots anchor the plant firmly in the ground, preventing it from being uprooted by wind or water.
- Storage: Some roots store food and nutrients (e.g., sweet potatoes, beets).
- Transportation: Roots transport absorbed water and nutrients to the stem and other parts of the plant.
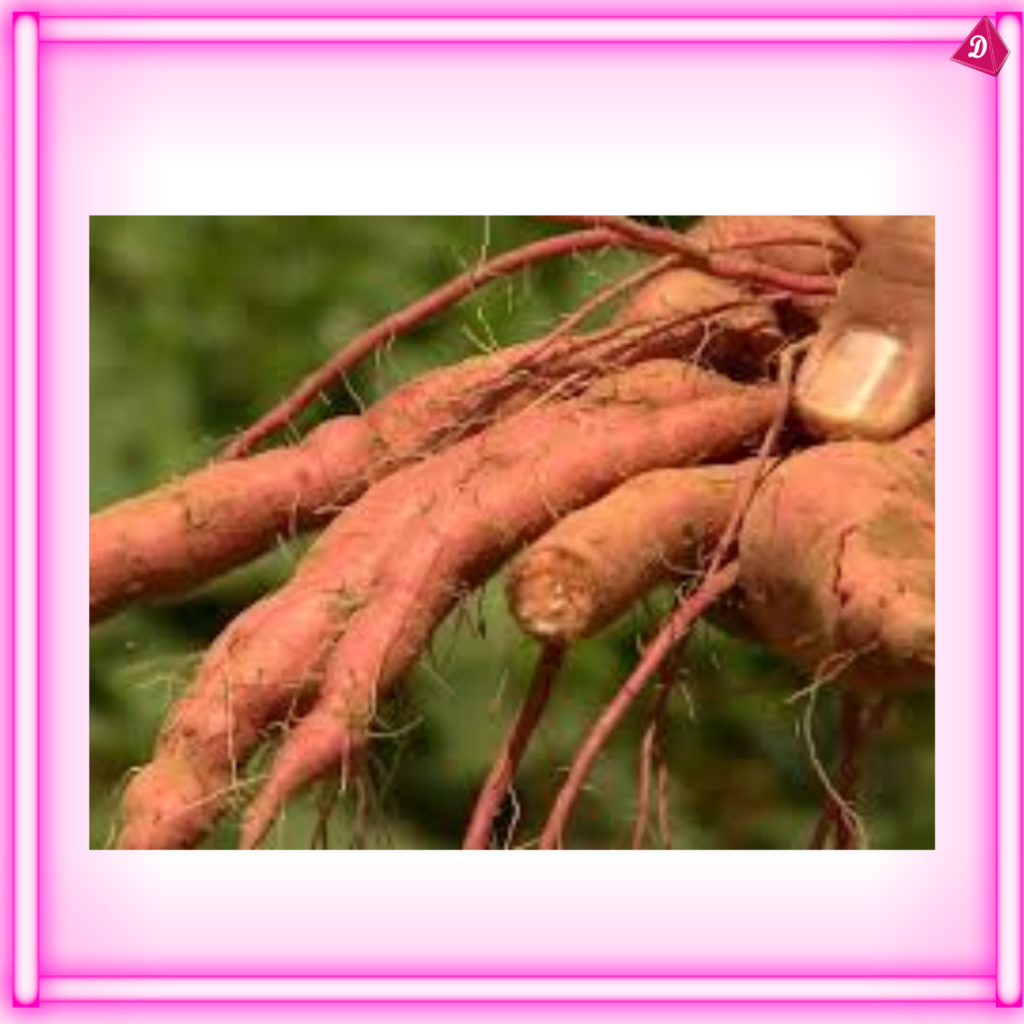
4. Root Modifications
- Storage Roots: Modified to store food, e.g., carrots, sweet potatoes.

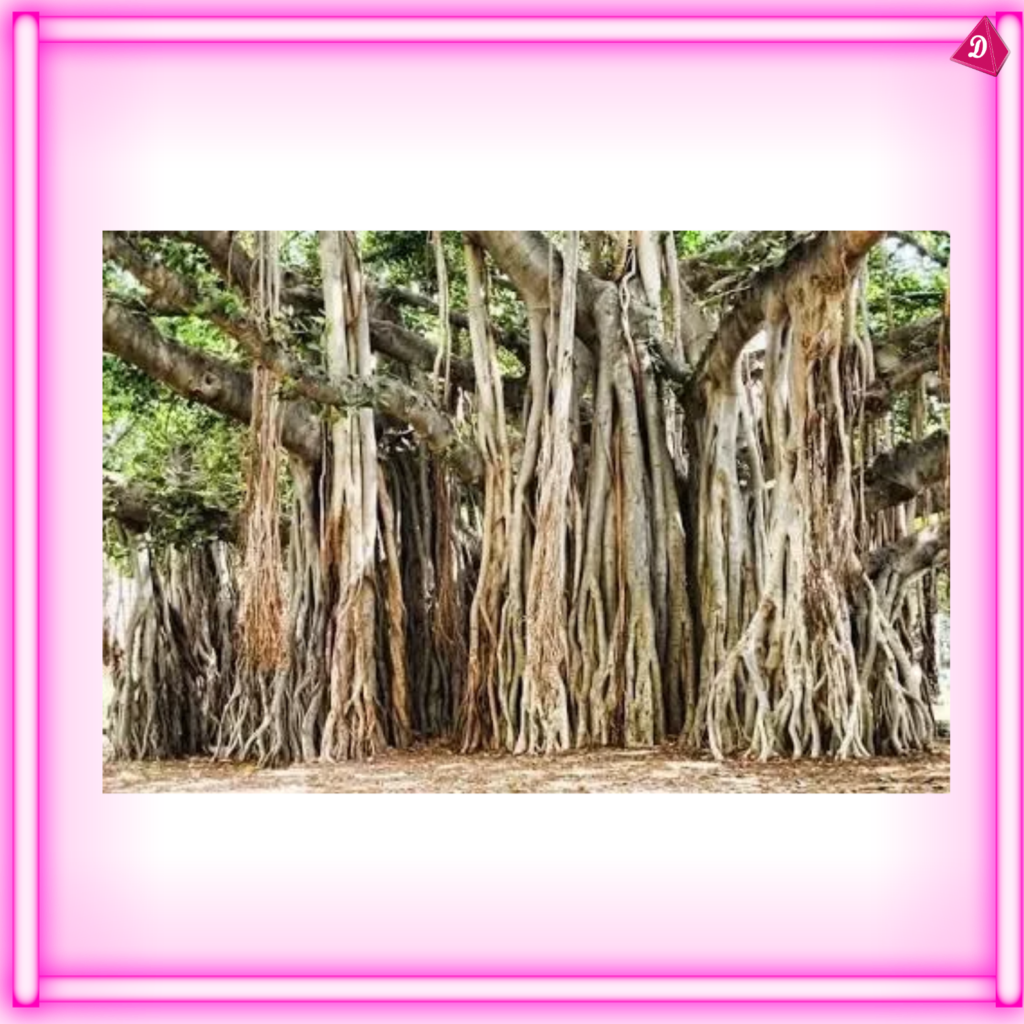
- Aerial Roots: Grow above the ground, e.g., roots of banyan trees.
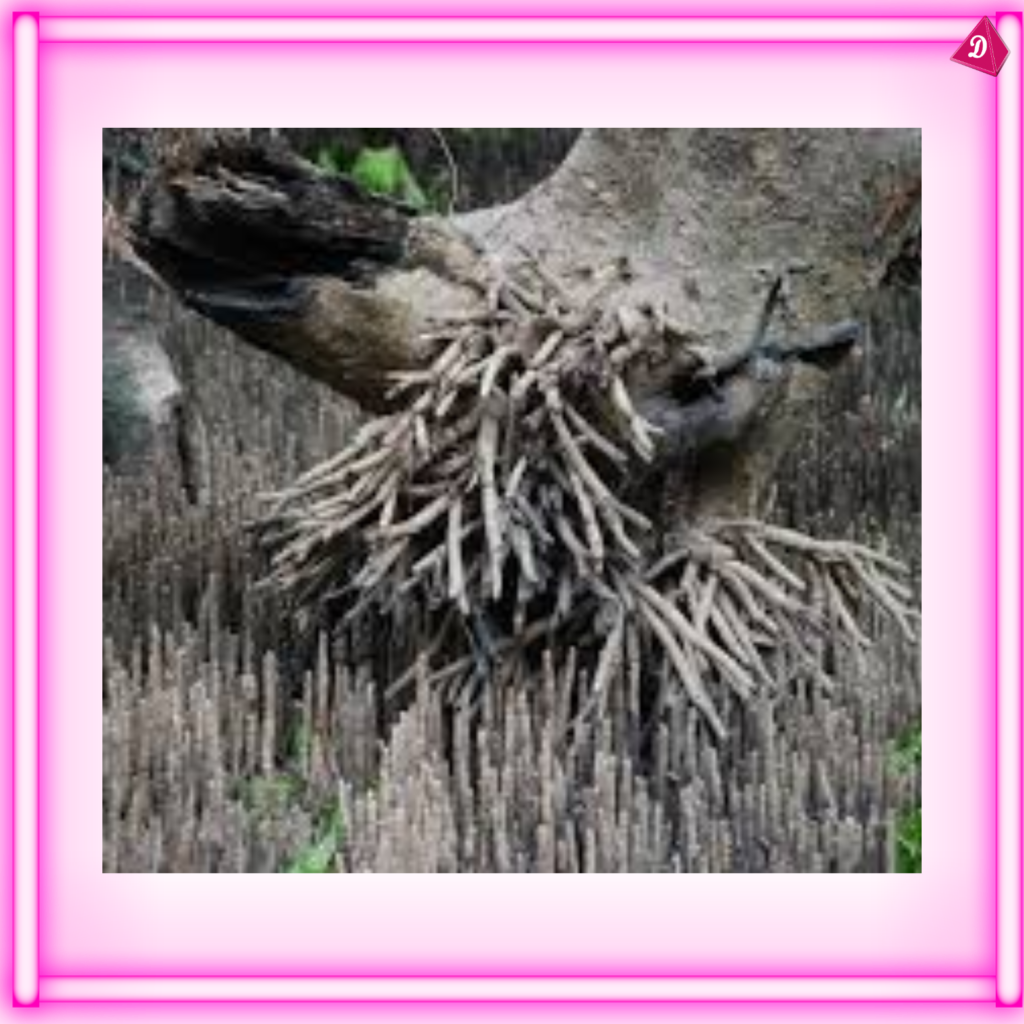

- Prop Roots: Provide extra support to the plant, e.g., roots of mangrove trees.

5. Root Hairs
- Definition: Tiny hair-like structures that increase the surface area for absorption.
- Function: Enhance the plant’s ability to absorb more water and nutrients.
6. Root Growth
- Growth Pattern: Roots grow downwards due to gravity (geotropism) and towards moisture (hydrotropism).
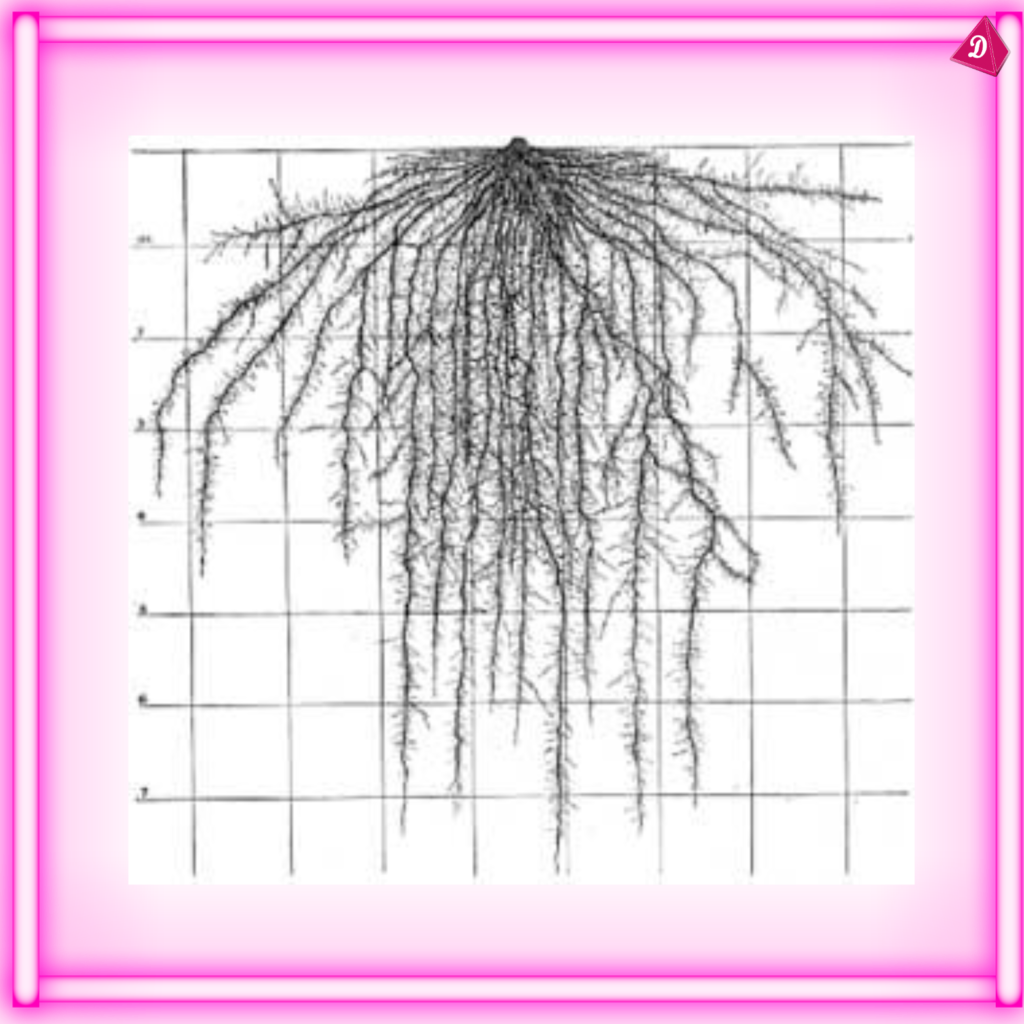

- Root Cap: The tip of the root is covered by a root cap, which protects it as it pushes through the soil.
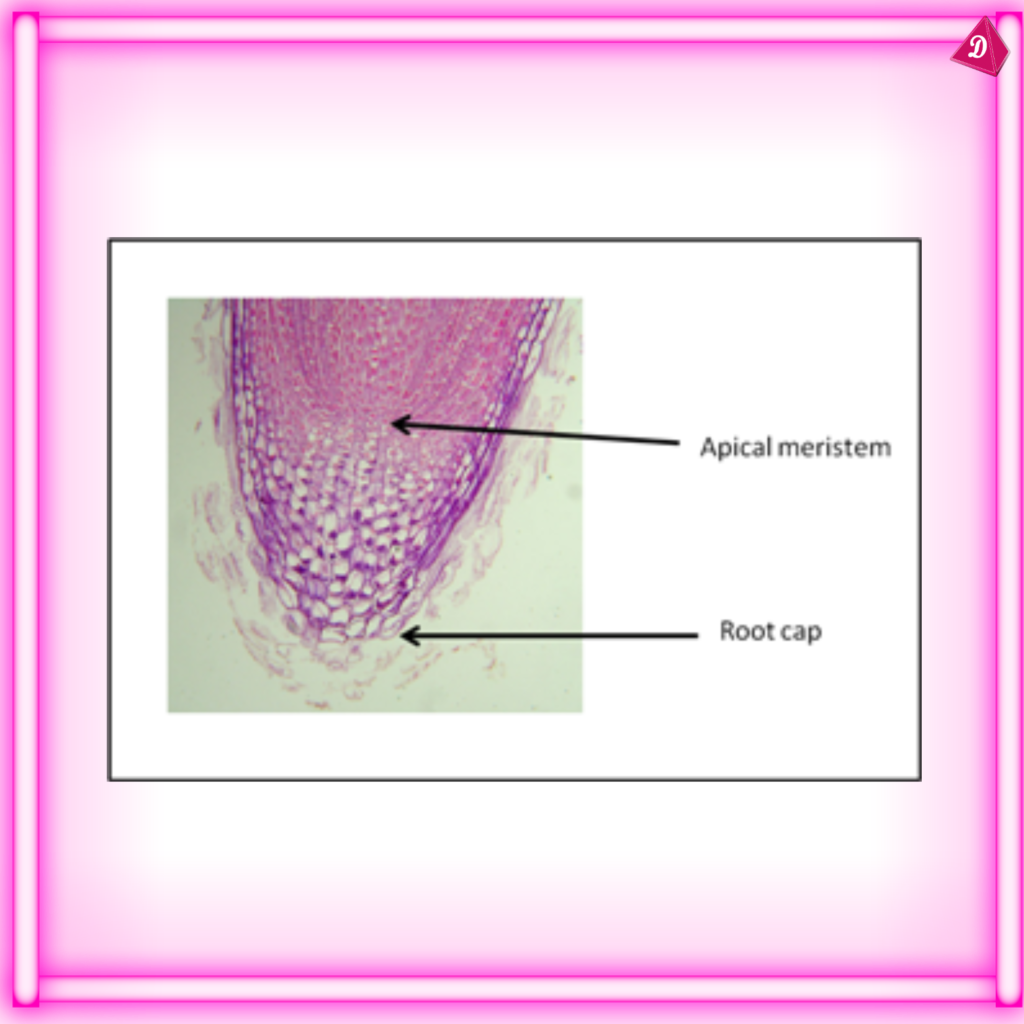
7. Role in Soil Health
- Soil Stabilization: Roots help prevent soil erosion by holding the soil together.
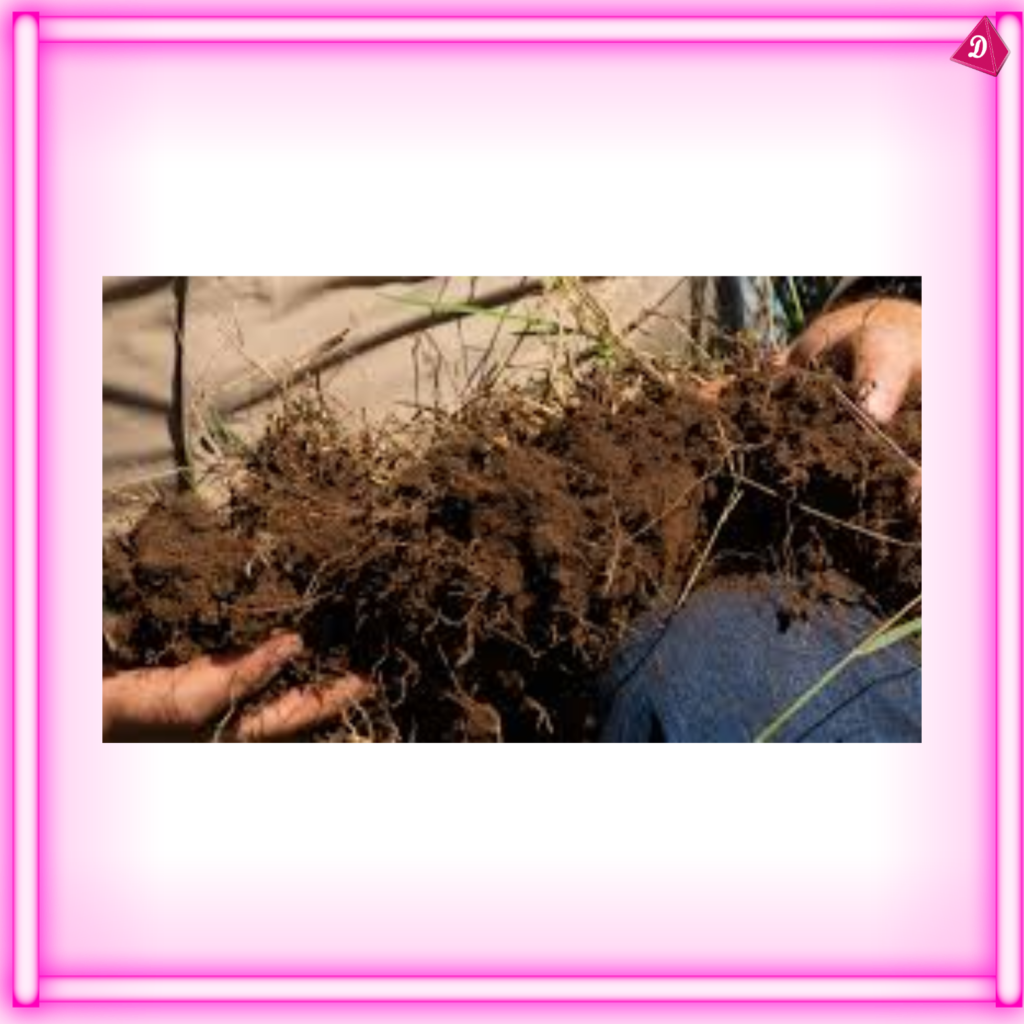

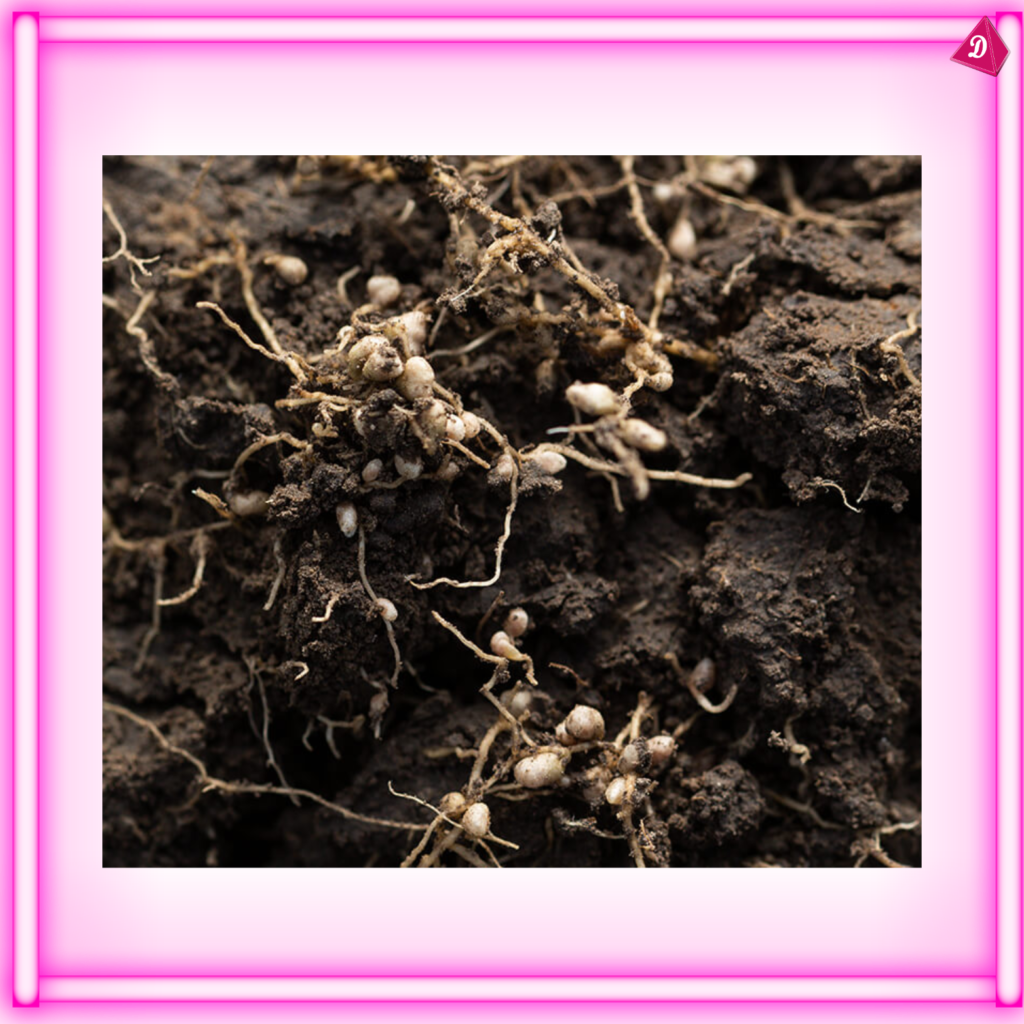
- Nutrient Cycling: Roots contribute to the cycling of nutrients within the soil ecosystem.

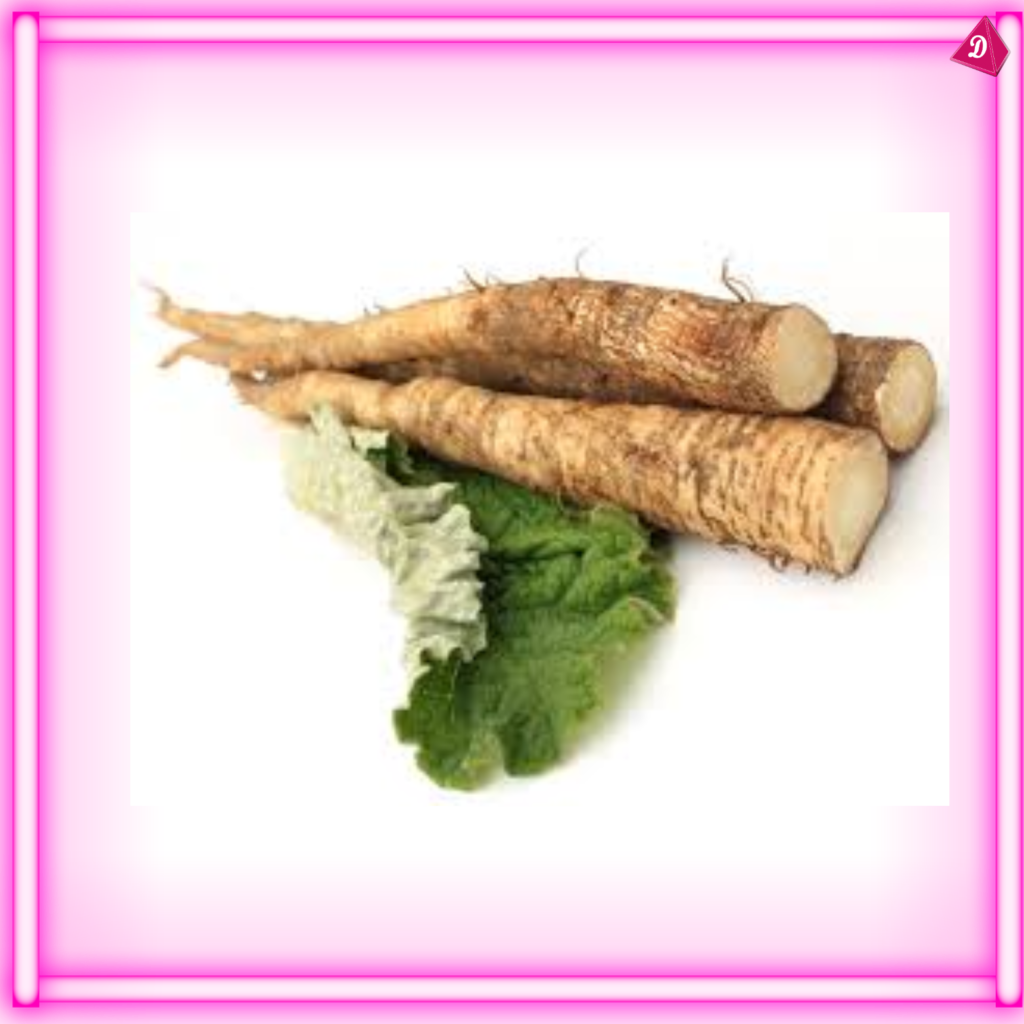
8. Human Uses
- Food: Many roots are edible and provide important food sources (e.g., potatoes, beets).
- Medicine: Some roots are used in traditional and modern medicine for their healing properties.

Let’s practice!

