Leaf
leaf by Delta publications
Key Notes :
1. Definition and Function
- Leaf: A leaf is an organ of a plant that is typically green and is attached to the stem or branch.
- Functions:
- Photosynthesis: Leaves are the main site for photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Transpiration: They release water vapor into the air, helping regulate water and nutrient flow.
- Gas Exchange: Leaves allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to enter and exit the plant through small openings called stomata.
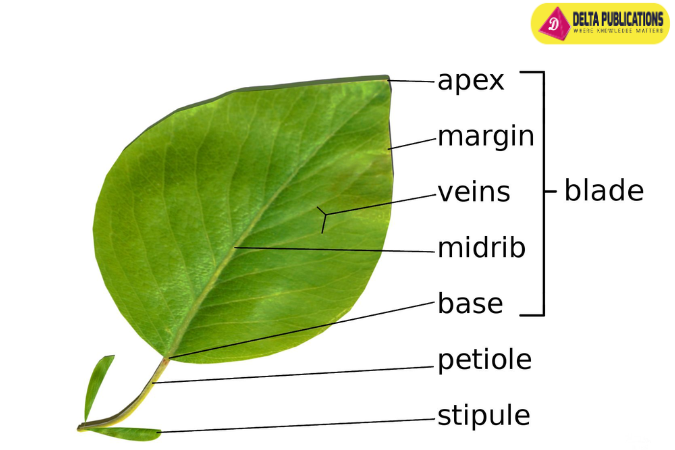
2. Structure of a Leaf
- Blade: The broad, flat part of the leaf.
- Petiole: The stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem.
- Veins: The network of vascular tissues that transport water, nutrients, and food throughout the leaf.
- Midrib: The central vein that runs through the leaf blade and supports it.
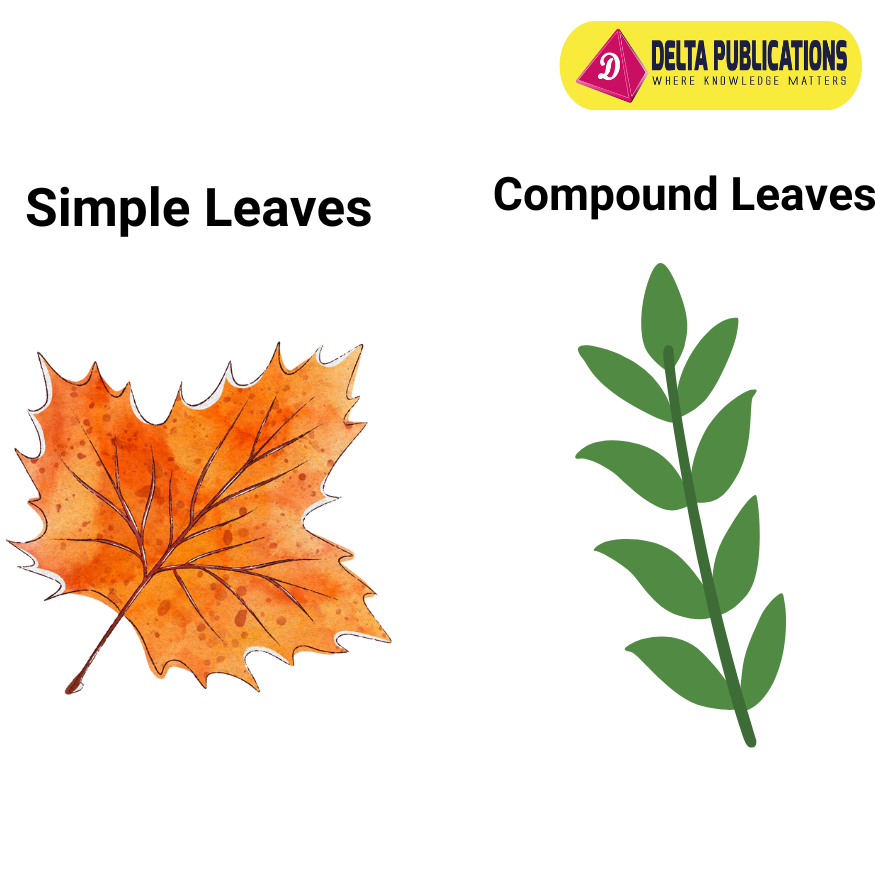
3. Types of Leaves
- Simple Leaves: Have a single, undivided blade (e.g., maple leaf).
- Compound Leaves: Have a blade divided into multiple leaflets (e.g., rose leaf).
4. Leaf Arrangements
- Alternate: A single leaf per node, alternating sides on the stem.
- Opposite: Two leaves per node, directly across from each other.
- Whorled: Three or more leaves per node, arranged in a circle.
5. Leaf Shapes and Sizes
- Shapes: Leaves come in various shapes such as oval, lance-shaped, heart-shaped, or needle-like.
- Sizes: Can vary from very small (e.g., grass) to very large (e.g., banana plant).
6. Leaf Adaptations
- Waxy Coating: Some leaves have a waxy layer to prevent water loss.
- Leaf Hairs: Can help reduce water loss and protect from herbivores.
- Shape and Size: Adapted to different environments; for example, desert plants have small leaves to reduce water loss.
7. Seasonal Changes
- Deciduous Leaves: Change color and fall off in autumn as part of the plant’s adaptation to cold or dry seasons.
- Evergreen Leaves: Remain green and functional throughout the year.
8. Economic and Ecological Importance
- Oxygen Production: Leaves are crucial for producing the oxygen we breathe.
- Food Source: Many leaves are edible and form part of the human diet (e.g., spinach, lettuce).
- Habitat: Leaves provide habitat and food for various insects and animals.
9. Leaf Diseases and Pests
- Diseases: Includes fungal infections like powdery mildew and bacterial infections.
- Pests: Insects like aphids and caterpillars can damage leaves.
Let’s practice!

