STEM
stem by Delta publications
Key Notes :
Definition: The stem is the main structural part of a plant that supports leaves, flowers, and fruits. It also connects the roots to the rest of the plant.
Functions of the Stem:
- Support: Holds up the plant, keeping it upright and allowing it to grow towards the light.
- Transport: Carries water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plant, and transports food made in the leaves to other parts.
- Storage: Some plants store nutrients and water in their stems.
Types of Stems:
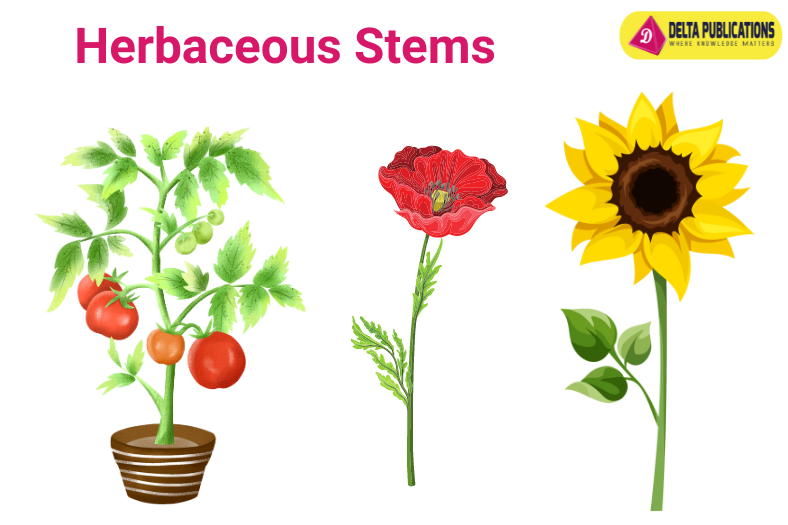
- Herbaceous Stems: Soft, green, and flexible, like those of a tomato or sunflower.
- Woody Stems: Hard and rigid, like those of trees and shrubs. They have a bark layer for protection.

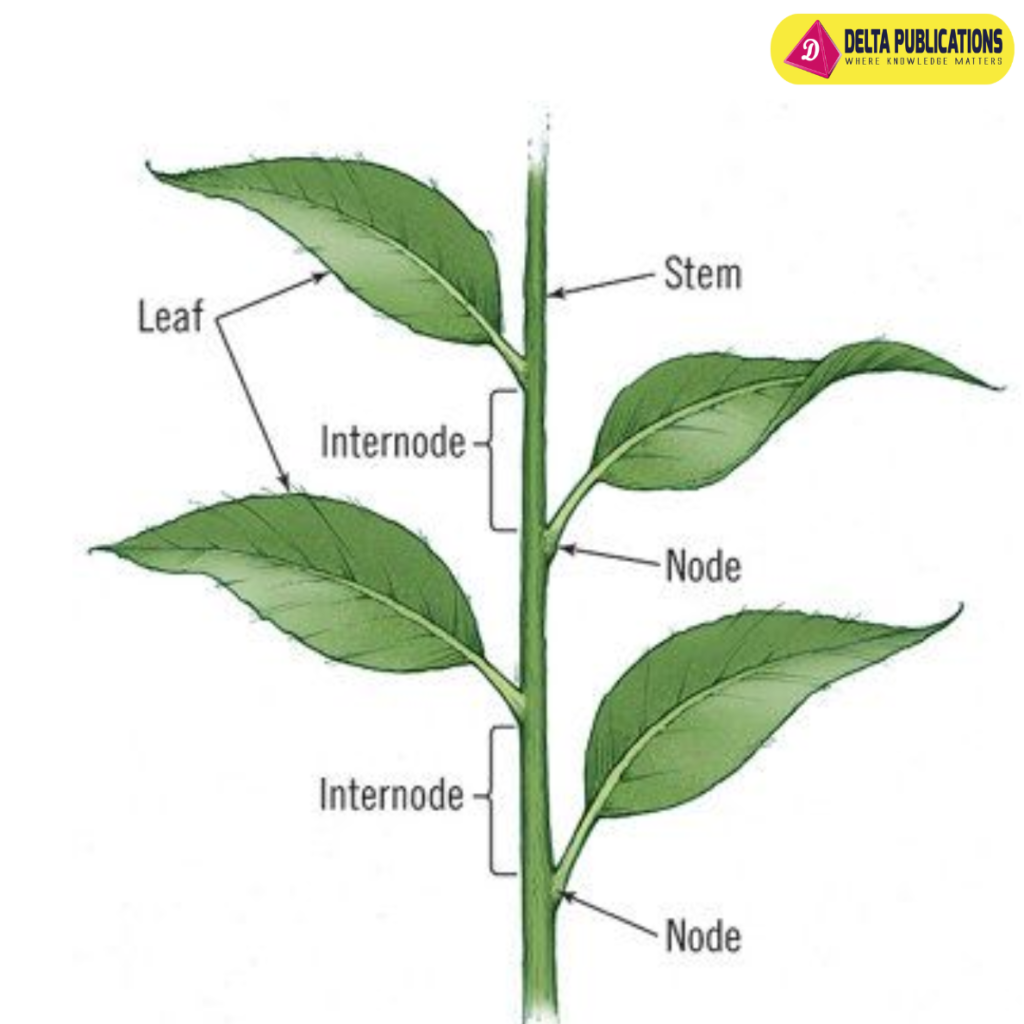
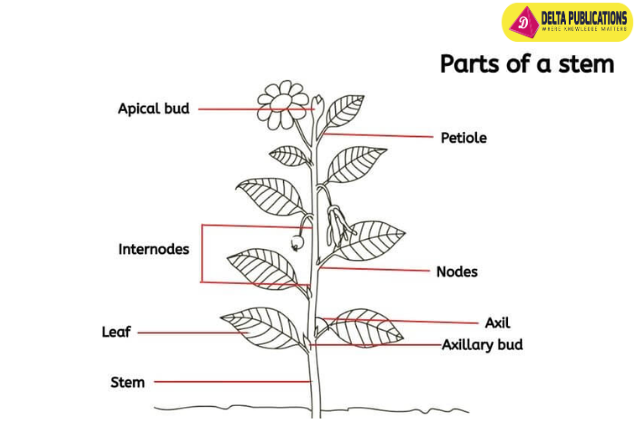
Parts of the Stem:
- Node: The point on the stem where leaves, branches, or flowers are attached.
- Internode: The segment of the stem between two nodes.
- Axil: The angle between the stem and the leaf stalk or branch.
Stem Modifications:
- Tendrils: Thin, coiling structures that help plants climb, such as in peas.
- Thorns: Sharp, pointed structures for protection, like those on roses.
- Runners: Horizontal stems that grow along the ground and produce new plants, as seen in strawberries.
Examples of Stems:
- Cactus Stems: Store water in their thick, fleshy stems.
- Potato Tubers: Modified stems that store nutrients underground.
Importance in Ecosystems: Stems play a crucial role in the plant’s ability to perform photosynthesis, reproduce, and interact with the environment.
Let’s practice!

