Methods of Separation
methods of seperation by Delta publications
Key Notes :
Introduction to Separation
- Purpose: Separating mixtures to obtain individual components.
- Mixtures: Two or more substances mixed together, like sand and salt.
Common Methods of Separation
1. Filtration
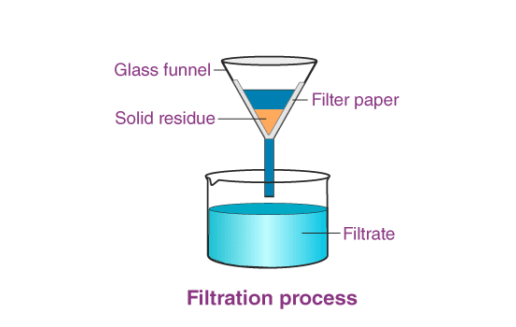
- Used For: Separating solids from liquids.
- Example: Sand from water.
- How It Works: A filter paper in a funnel traps solid particles while the liquid passes through.
2. Sifting

- Used For: Separating larger solid particles from smaller ones.
- Example: Flour from lumps.
- How It Works: A sieve or strainer allows smaller particles to pass through while retaining larger ones.
3. Evaporation

- Used For: Separating a solid dissolved in a liquid.
- Example: Salt from seawater.
- How It Works: Heating the liquid causes it to evaporate, leaving the solid behind.
4. Distillation
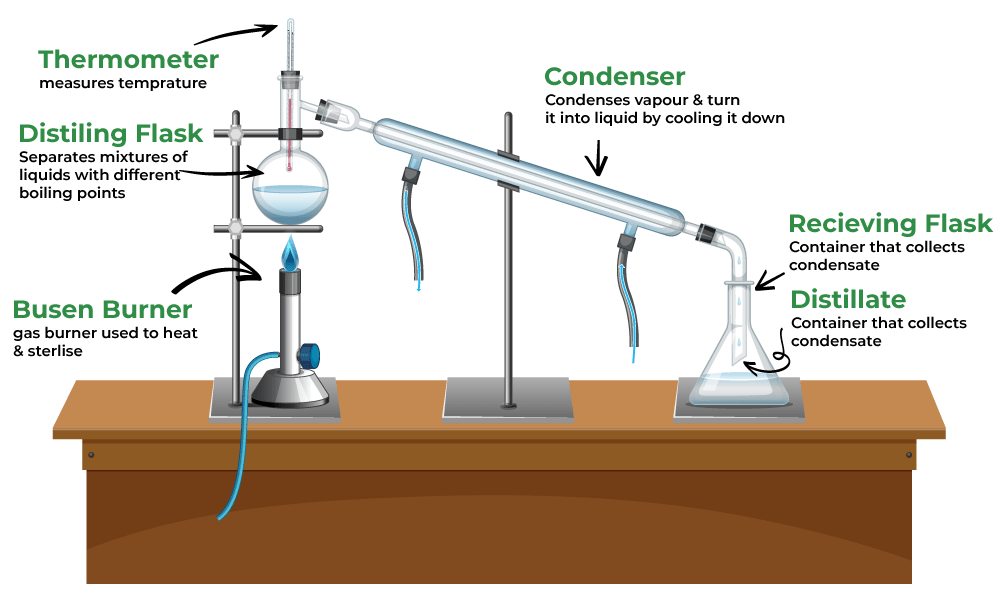
- Used For: Separating liquids with different boiling points.
- Example: Separating alcohol from a mixture.
- How It Works: Heating the mixture causes the liquid with the lower boiling point to evaporate first, then it is condensed back into a liquid.
5. Magnetic Separation
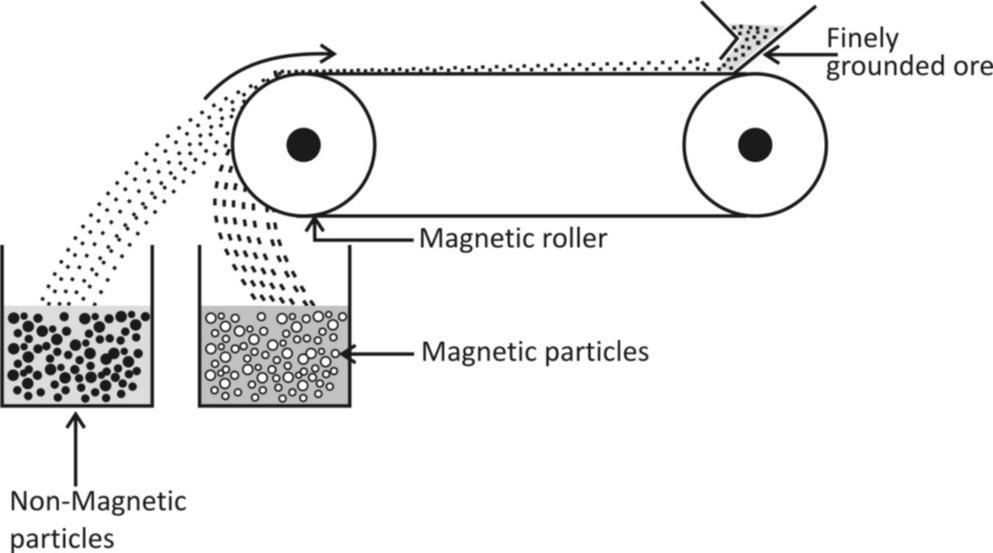
- Used For: Separating magnetic materials from non-magnetic ones.
- Example: Iron filings from sand.
- How It Works: A magnet attracts the magnetic materials, leaving the non-magnetic materials behind.
6. Centrifugation

- Used For: Separating substances based on density.
- Example: Separating cream from milk.
- How It Works: Spinning the mixture at high speeds causes denser substances to move outward and separate.
7. Decantation
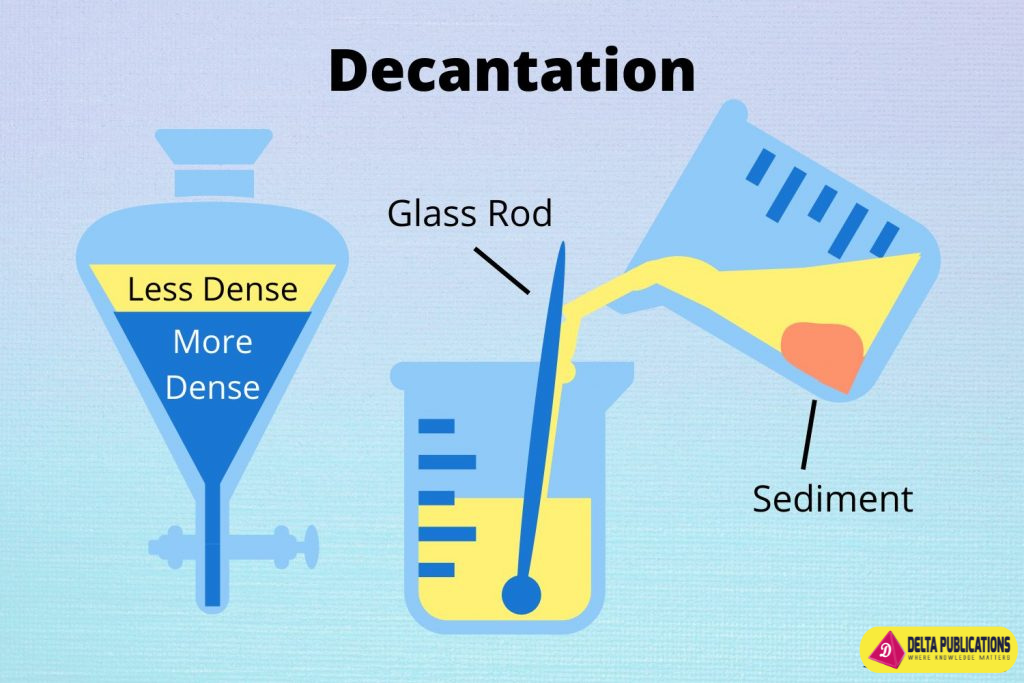
- Used For: Separating liquids from solids or separating two liquids with different densities.
- Example: Oil from water.
- How It Works: Pouring off the top layer of liquid after allowing the mixture to settle.
Application and Examples
- Practical Uses: Purifying water, recycling, cooking processes.
- Everyday Examples: Making lemonade, separating salad ingredients, cleaning up spills.
Summary
- Different methods are suited to different types of mixtures and substances.
- Understanding these methods helps in everyday life and in scientific experiments.
Lets practice!

