introduction
Key Notes :
Definition:
- Separation of substances refers to the process of dividing or removing different components from a mixture to make them pure or separate the useful substances from the unwanted ones.
Purpose of Separation:
- To remove impurities or harmful substances.
- To separate useful substances from a mixture (e.g., salt from seawater).
- To obtain a pure substance from a mixture.
Types of Mixtures:

- Homogeneous mixture: A mixture in which the components are evenly distributed (e.g., salt in water).
- Heterogeneous mixture: A mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed (e.g., sand in water).
Need for Separation:
- Different substances in a mixture may have different properties (e.g., size, weight, solubility) which allow them to be separated.
- Separation is necessary in everyday life (e.g., separating rice from small stones, cream from milk).
Common Methods of Separation:
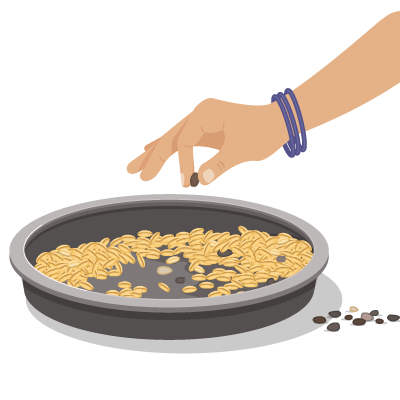
Handpicking: Used when the substances are large enough to be picked by hand (e.g., separating pebbles from grains).

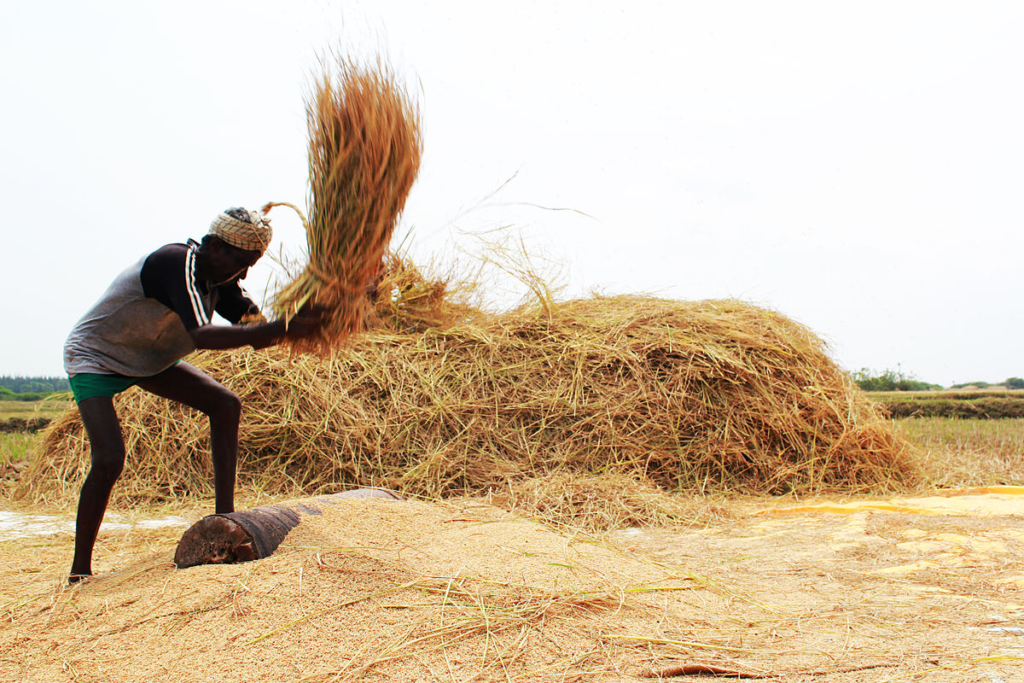
Threshing: Used to separate grains from stalks.

Winnowing: Used to separate lighter particles from heavier ones using wind (e.g., separating husk from grain).

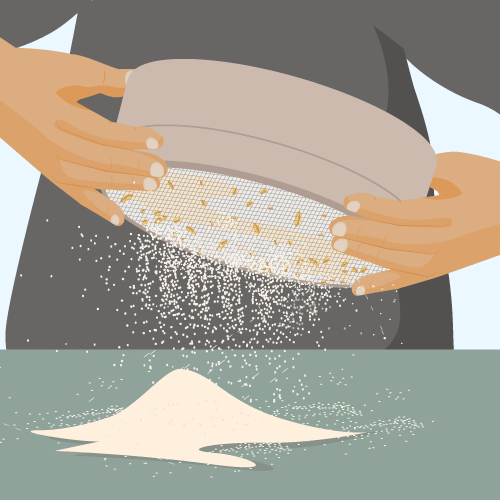
Sieving: Used to separate particles of different sizes using a sieve (e.g., separating flour from bran).

Sedimentation and Decantation: Sedimentation allows heavier particles to settle at the bottom of a liquid, and decantation separates the liquid from the solid.
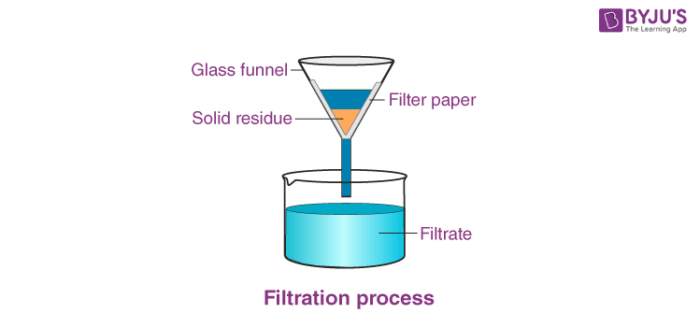
Filtration: Used to separate insoluble solids from liquids (e.g., separating sand from water).
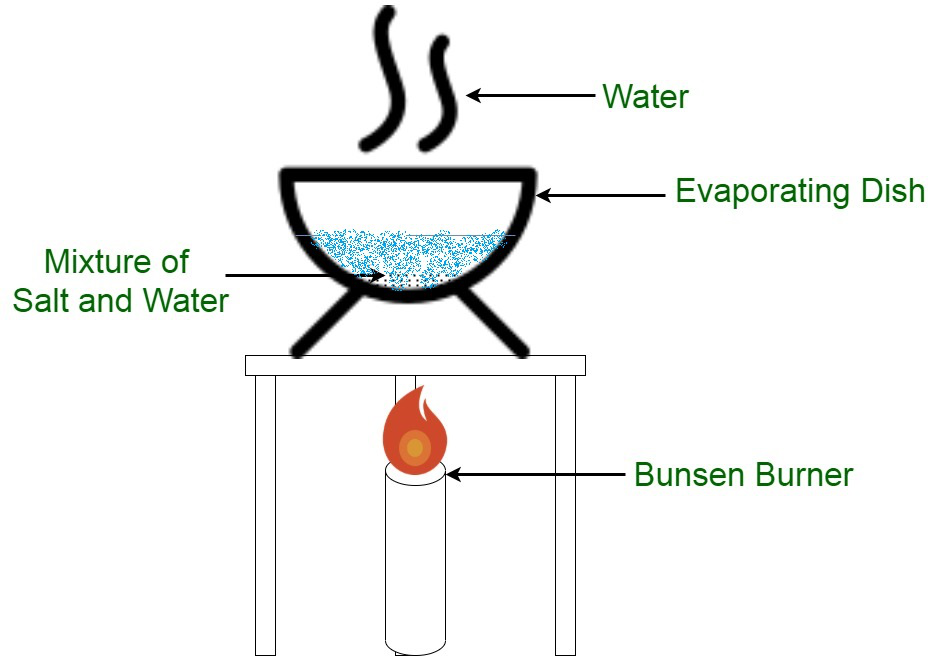
Evaporation: Used to separate a soluble solid from a liquid (e.g., obtaining salt from seawater).
Distillation: Used to separate two liquids with different boiling points (e.g., separating alcohol from water).

Application in Daily Life:
- Purifying drinking water.
- Separating solid waste from liquids in the kitchen.
- Processing raw materials in industries.
Key Concepts:
- Soluble substances dissolve in liquids (e.g., salt in water), whereas insoluble substances do not (e.g., sand in water).
- Different methods of separation are chosen based on the physical properties of the substances in the mixture, such as size, solubility, weight, and boiling point.
Let’s practice!

