Properties Of Materials
Key Notes :
Definition of Materials
- Materials are substances used to make objects or products. They can be natural (like wood and cotton) or man-made (like plastic and glass).
Types of Materials

- Common materials include wood, metal, plastic, fabric, glass, and rubber. Each has specific properties that make them suitable for different uses.
Properties of Materials
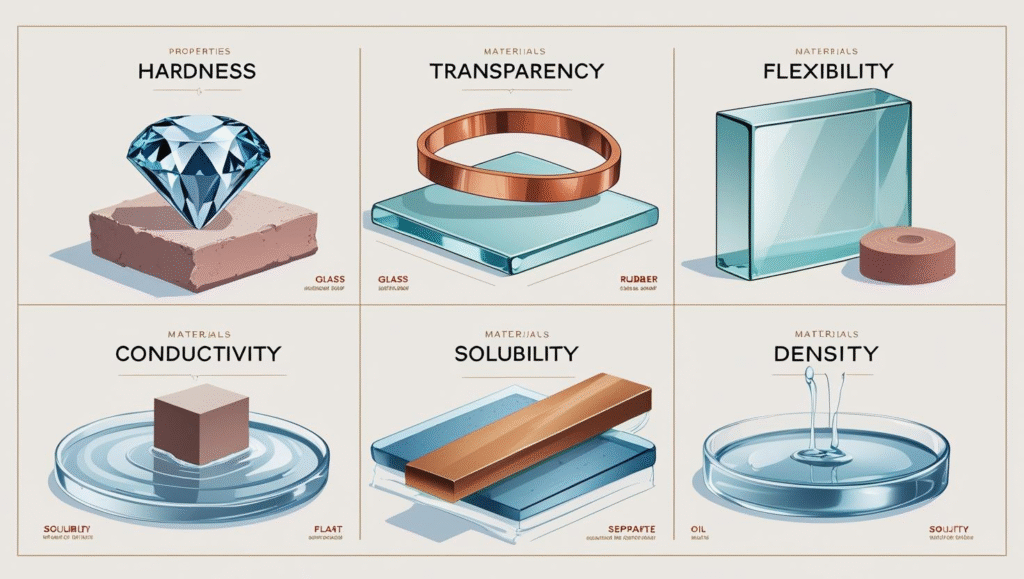
- Hardness: Measures how resistant a material is to being scratched or dented. Metals like iron are hard, while rubber is soft.
- Transparency: Defines how much light passes through a material. Transparent materials (like glass) allow light to pass, while opaque materials (like wood) do not.
- Flexibility: Describes how easily a material bends without breaking. Rubber and fabric are flexible, while glass and metals are rigid.
- Conductivity: Refers to a material’s ability to conduct heat or electricity. Metals are good conductors, while plastic and rubber are poor conductors (insulators).
- Solubility: The ability of a material to dissolve in a liquid (usually water). For example, sugar is soluble in water, but sand is not.
- Density: The mass per unit volume of a material. Objects made from dense materials (like steel) are heavier than those made from less dense materials (like foam).
Importance of Properties in Everyday Use
- Understanding the properties of materials helps in choosing the right material for specific uses, such as building construction, clothing, and packaging.
Material Changes
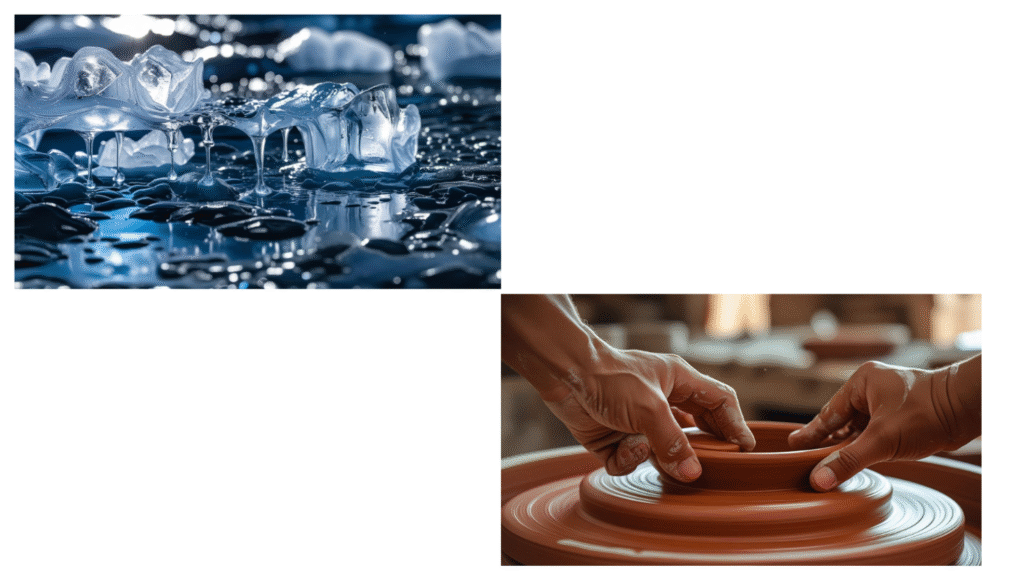
- Materials can change their properties through processes like heating, cooling, or mixing with other materials, which may result in new materials with different properties (e.g., melting ice, baking clay).

Let’s Practice!

