Some Plant Fibres
some plant fibers by Delta publications
Key Notes :
What are Plant Fibers?
- Plant fibers are natural fibers obtained from various parts of plants. These fibers are used in making textiles, ropes, and other materials.
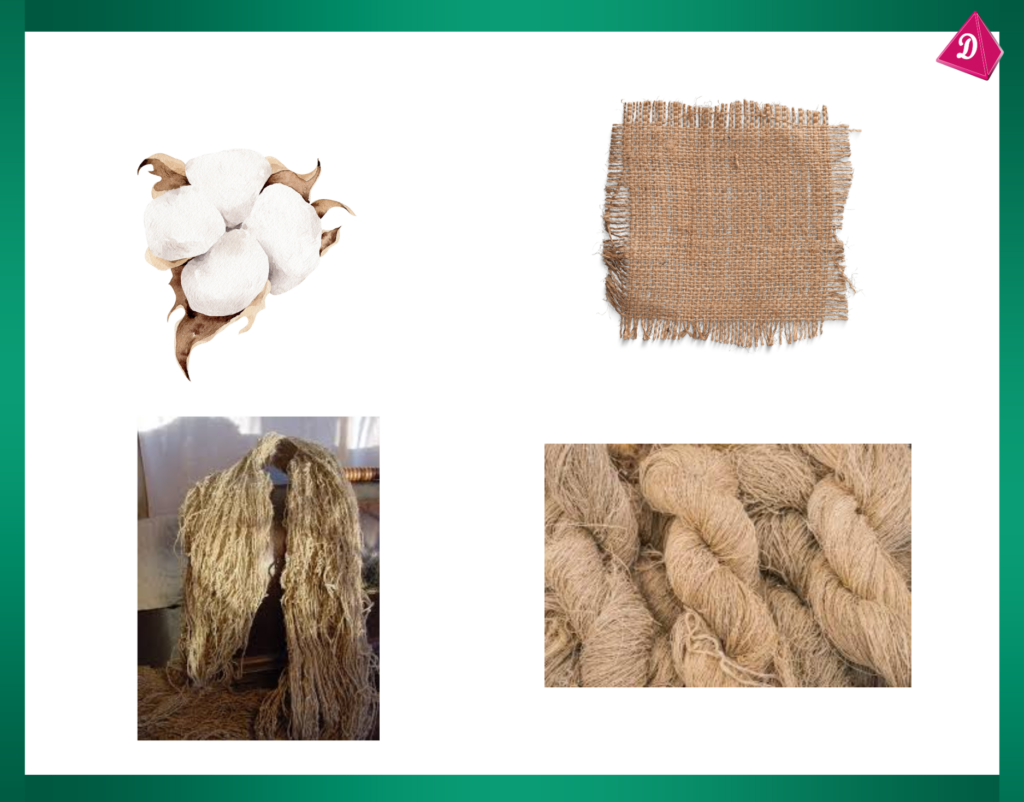

Types of Plant Fibers
- Cotton:
- Source: Cotton plant.
- Characteristics: Soft, absorbent, and breathable.
- Uses: Making clothes, towels, bed sheets, and cotton balls.
- Cultivation: Grown in warm climates with plenty of sunshine.
- Jute:
- Source: Jute plant.
- Characteristics: Strong, coarse, and biodegradable.
- Uses: Making burlap bags, ropes, mats, and eco-friendly packaging.
- Cultivation: Grown in tropical regions with high rainfall.

- Linen:
- Source: Flax plant.
- Characteristics: Durable, absorbent, and has a natural luster.
- Uses: Making clothing, tablecloths, napkins, and bed linens.
- Cultivation: Grown in temperate climates with well-drained soil.
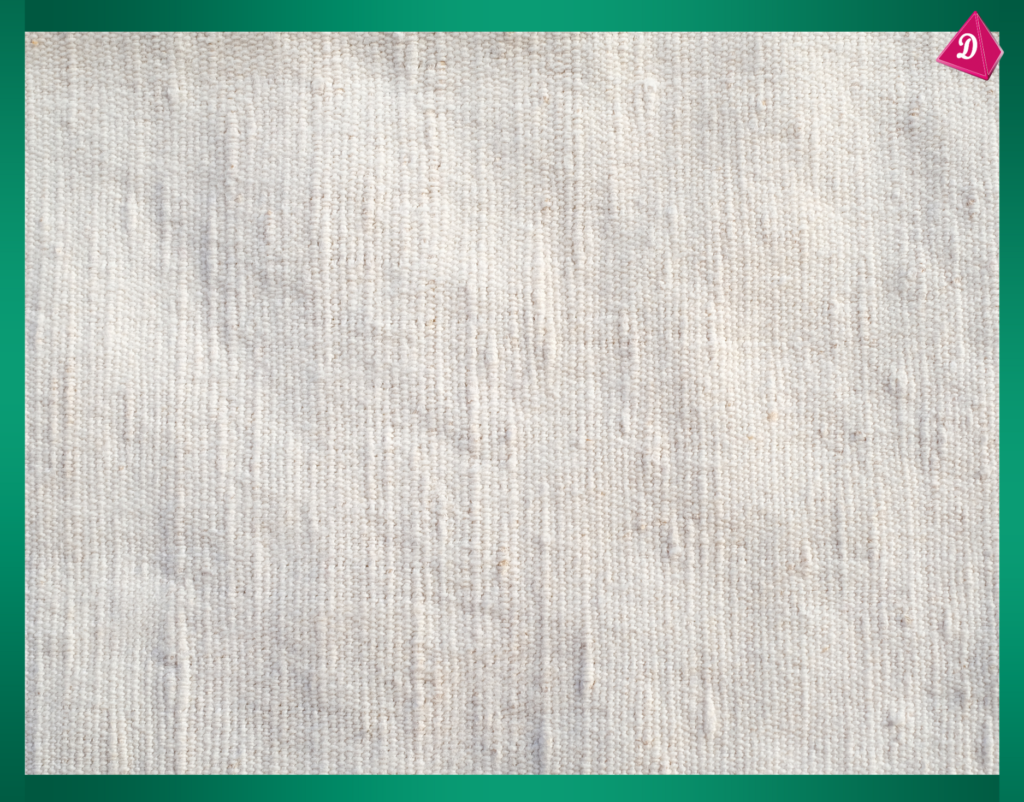

- Hemp:
- Source: Hemp plant.
- Characteristics: Strong, durable, and resistant to mold.
- Uses: Making ropes, clothing, biodegradable plastics, and building materials.
- Cultivation: Grown in various climates, requires minimal pesticides.

- Sisal:
- Source: Agave plant.
- Characteristics: Stiff, strong, and durable.
- Uses: Making ropes, mats, rugs, and agricultural twine.
- Cultivation: Grown in arid and semi-arid regions.

- Flax:
- Flax fibres are obtained from the flax plant and are used to produce linen fabric.
- Linen is strong, absorbent, and used for making clothes, bedsheets, and tablecloths.

- Coir:
- Coir is a fibre obtained from the outer shell (husk) of the coconut.
- It is strong and water-resistant, often used for making doormats, brushes, and ropes.

Importance of Plant Fibers
- Eco-friendly: Plant fibers are biodegradable and have a lower environmental impact compared to synthetic fibers.
- Renewable Resource: Plant fibers are sourced from plants that can be replanted and harvested annually.
- Versatility: Used in a wide range of products from textiles to industrial applications.
- Cultural Significance: Many cultures have traditional uses for plant fibers, contributing to local economies and heritage.

Steps in Processing Plant Fibers
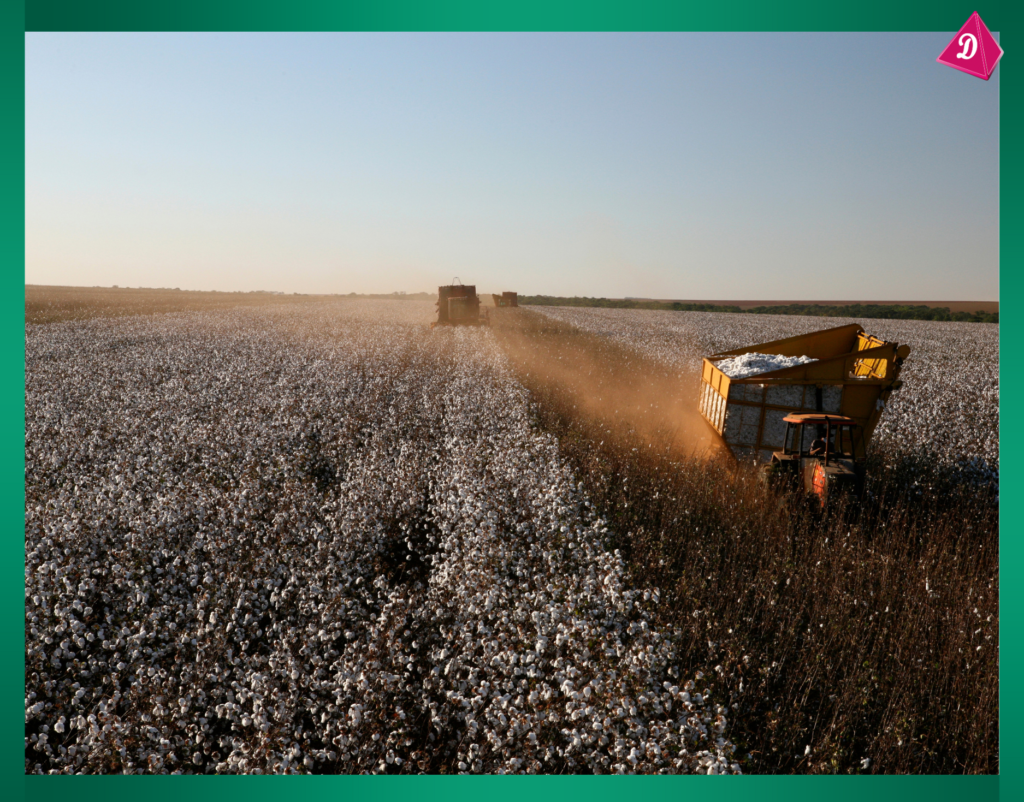
- Harvesting: Collecting the plant material (e.g., cotton bolls, jute stalks).

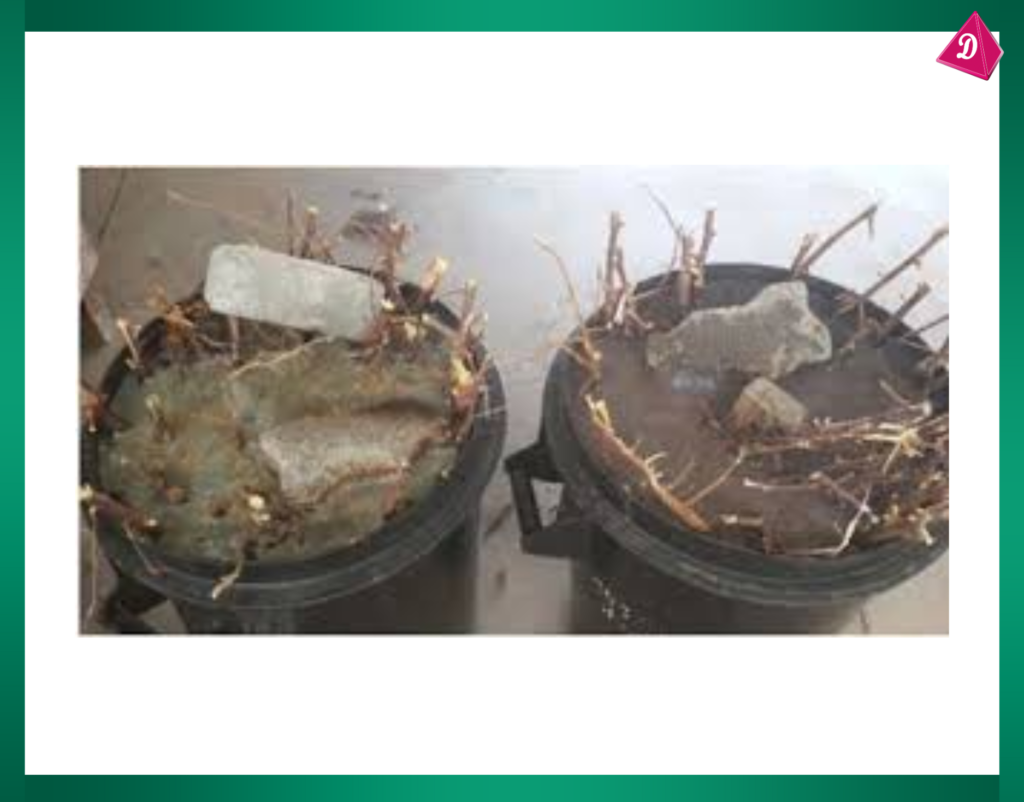
- Retting: Soaking the plant material in water to separate the fibers from the stem.

- Scutching: Removing the woody parts from the fibers.

- Spinning: Twisting the fibers into yarn or thread.

- Weaving/Knitting: Interlacing the yarn to create fabric.

Benefits of Using Plant Fibers
- Breathability: Plant fibers like cotton and linen are breathable and comfortable to wear.
- Absorbency: Excellent at absorbing moisture, making them ideal for towels and bedding.
- Strength: Some plant fibers, such as hemp and sisal, are very strong and durable, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Biodegradability: Environmentally friendly as they decompose naturally without causing pollution.
Let’s practice!

