Types of angles
Key Notes :
Here’s a simple guide to the different types of angles, along with some examples and key points:
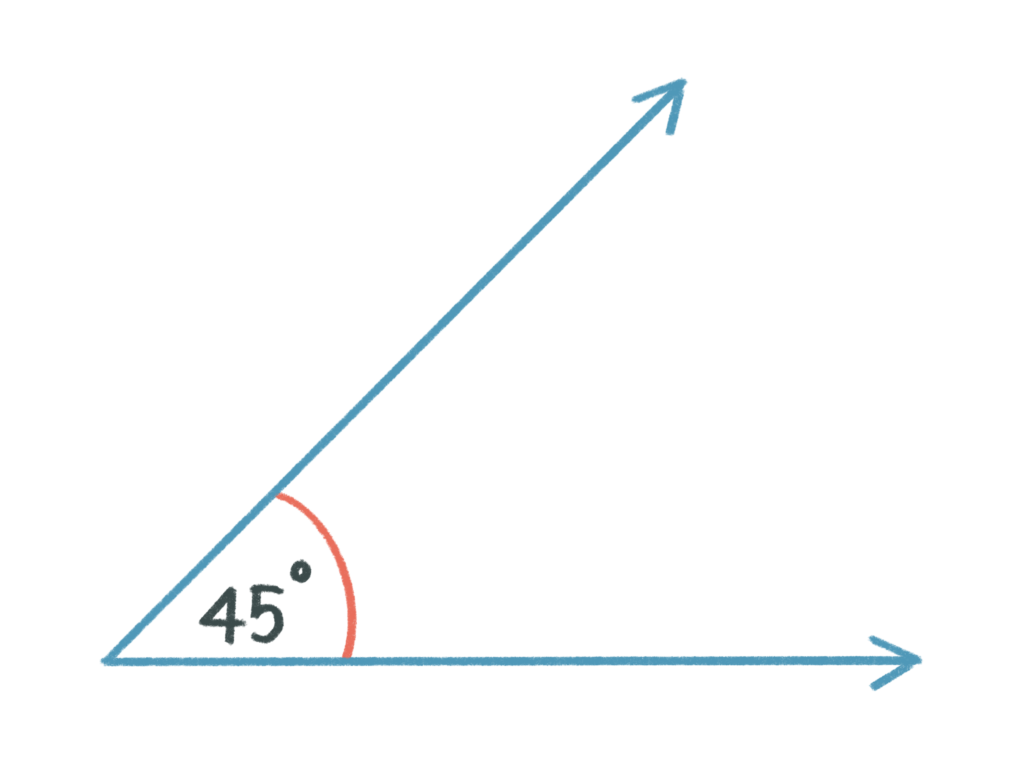
Acute Angle
- Definition: An angle that measures less than 90 degrees.
- Real-Life Example: The angle formed when you slightly open a book.
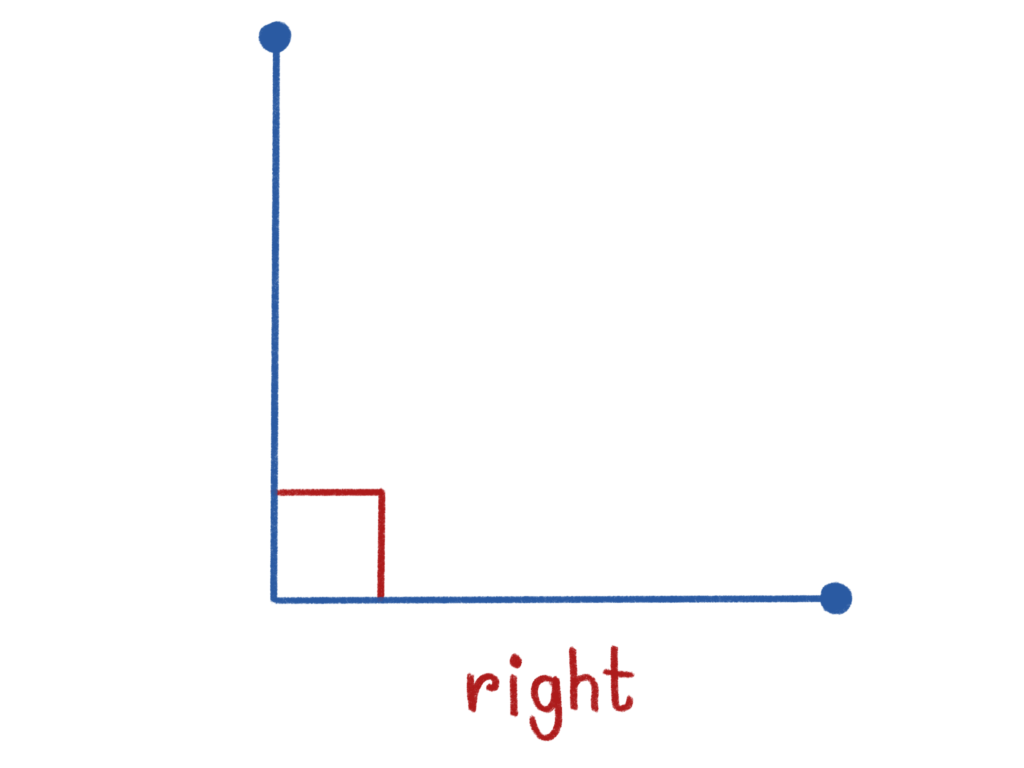
Right Angle
- Definition: An angle that measures exactly 90 degrees.
- Real-Life Example: The angle formed by the edges of a piece of paper.
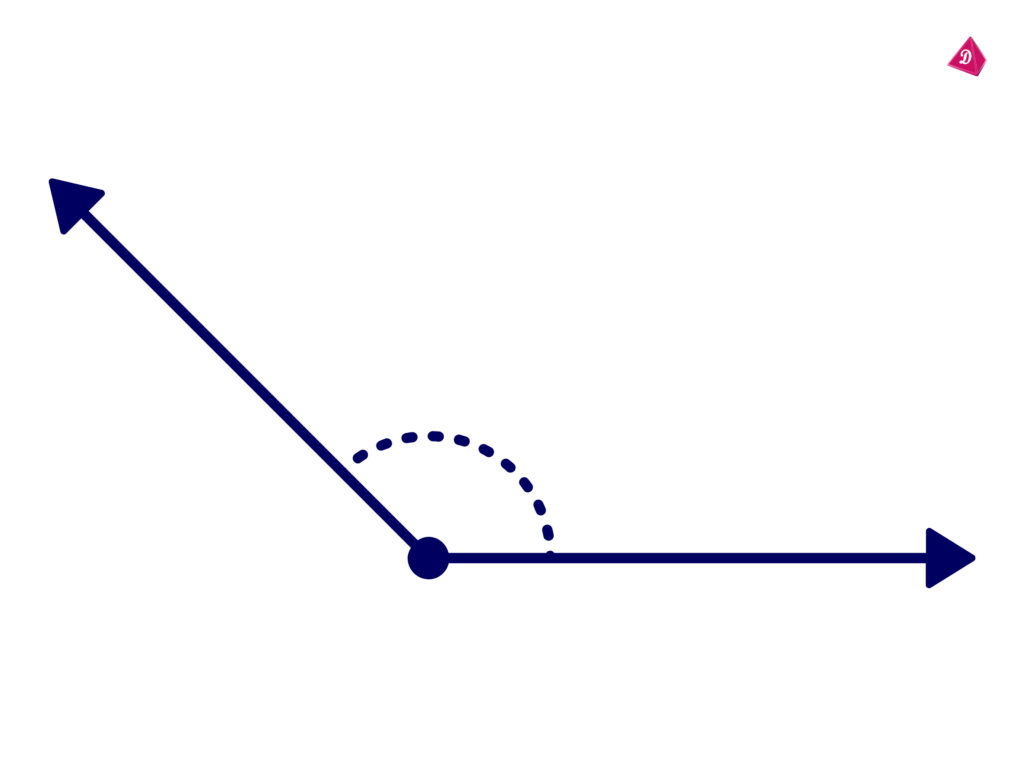
Obtuse Angle
- Definition: An angle that measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
- Real-Life Example: The angle formed when a door is half-open.
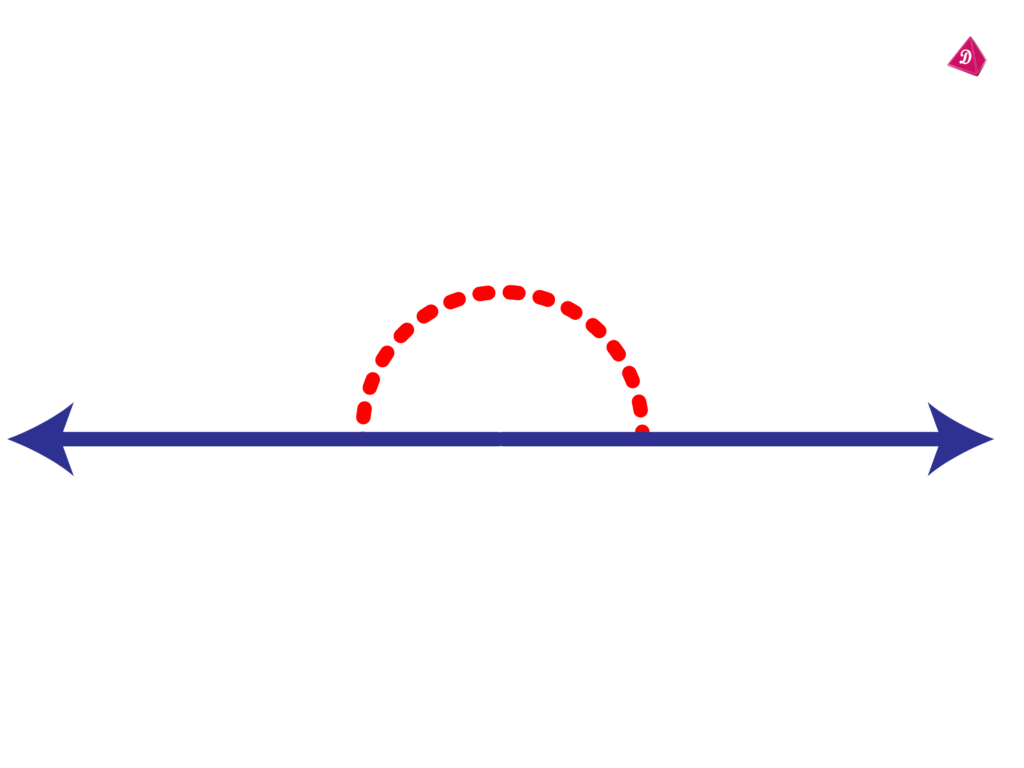
Straight Angle
- Definition: An angle that measures exactly 180 degrees.
- Real-Life Example: The angle formed by the hands of a clock at 6:00.
Reflex Angle
- Definition: An angle that measures more than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
- Real-Life Example: The angle formed when you open a door wide, more than half but not all the way around.

Full Rotation/Complete Angle
- Definition: An angle that measures exactly 360 degrees.
- Real-Life Example: The angle formed by the hands of a clock after completing one full rotation (12 hours).
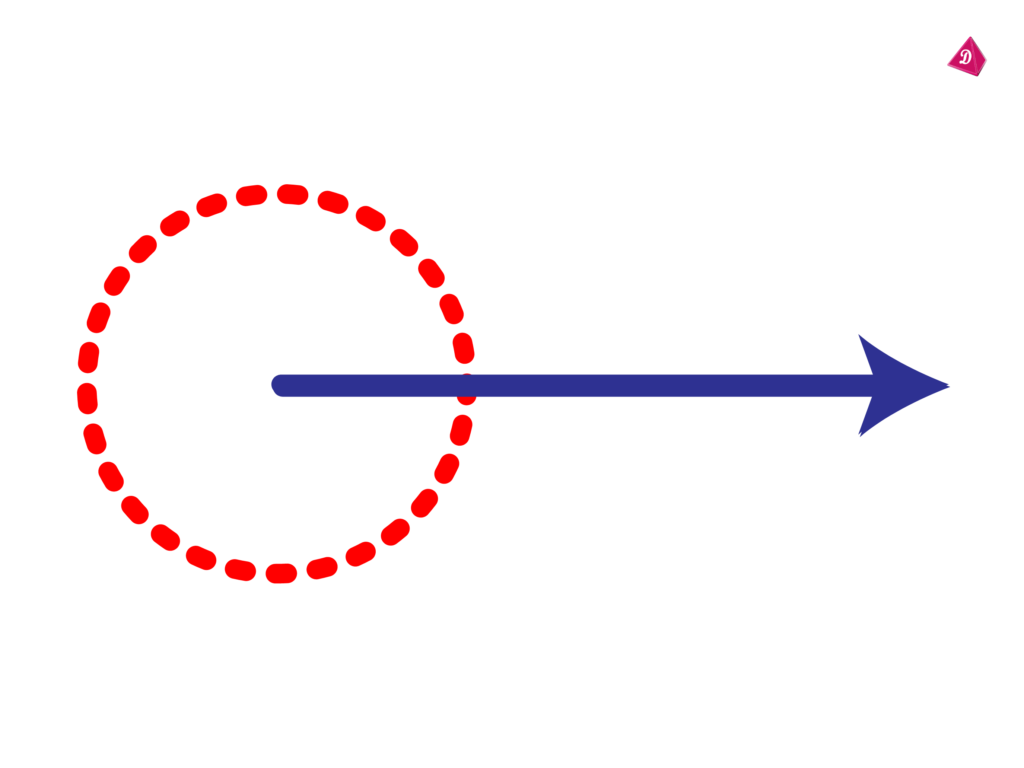
Learn with an example
🎯 Is this angle greater than, equal to, or less than a right angle?
- greater than a right angle
- equal to a right angle
- less than a right angle
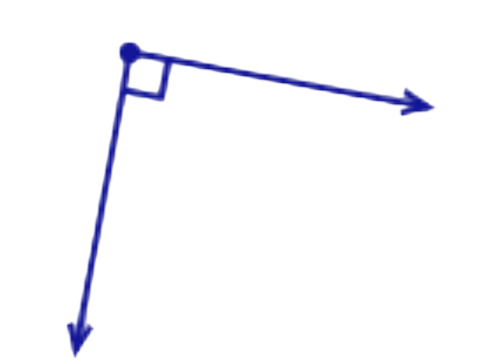
- Look at this angle:
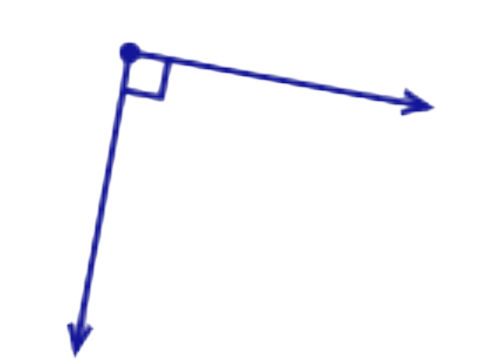
- This angle is equal to a right angle. Notice the right angle symbol in the corner.
🎯 Is this angle greater than, equal to, or less than a right angle?
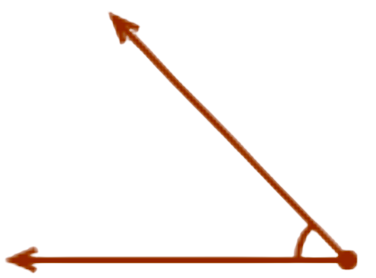
- greater than a right angle
- equal to a right angle
- less than a right angle
- Look at this angle:
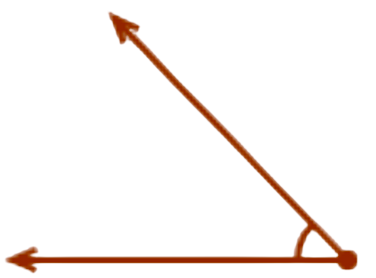
- This angle is less than a right angle.
🎯 Is this angle greater than, equal to, or less than a right angle?

- greater than a right angle
- equal to a right angle
- less than a right angle
- Look at this angle:
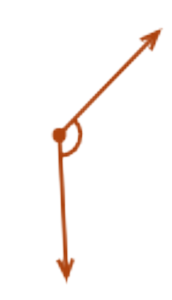
- This angle is greater than a right angle.
Let’s practice!🖊️

