Living things under microscope
Key Notes :
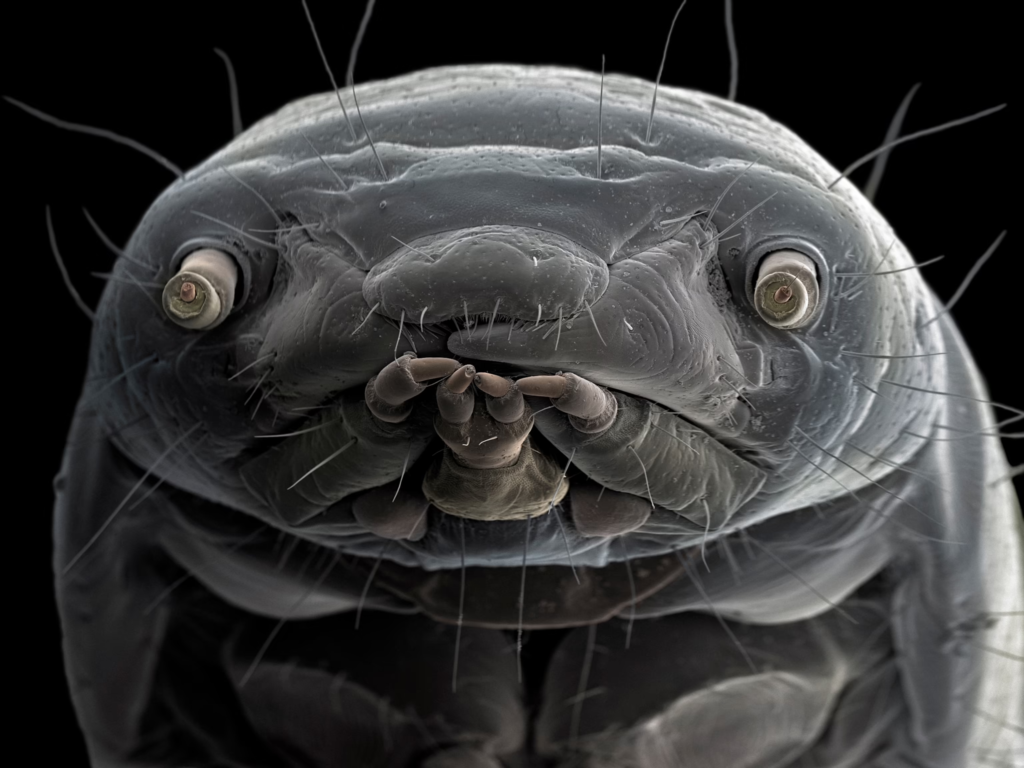
Introduction to Microscopy:
Microscopes are scientific instruments that allow us to see very small objects that are not visible to the naked eye.
There are different types of microscopes, including light microscopes and electron microscopes.
The Microscopic World:
Microscopes reveal a hidden world of tiny organisms and structures.
Living things that are too small to be seen without a microscope include bacteria, protozoa, and microscopic algae.
Microscopic Living Things:
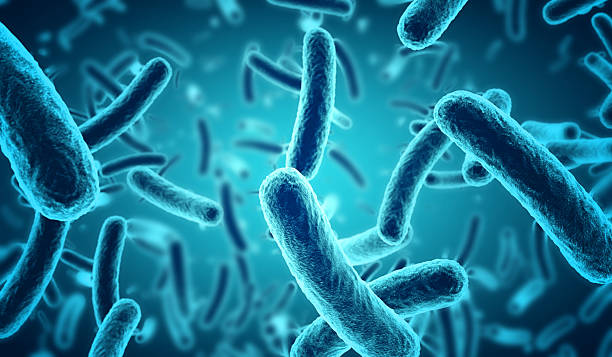
- Bacteria: These single-celled organisms are ubiquitous and come in various shapes, such as cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), and spirilla (spiral-shaped). Some bacteria are harmless or even beneficial, while others can cause diseases.
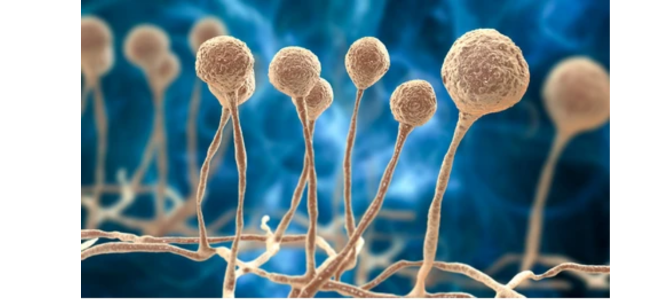
- Fungi: Fungi can exist as single-celled yeasts or multicellular molds and mushrooms. Under the microscope, you might observe fungal hyphae (filaments) and reproductive structures such as spores.
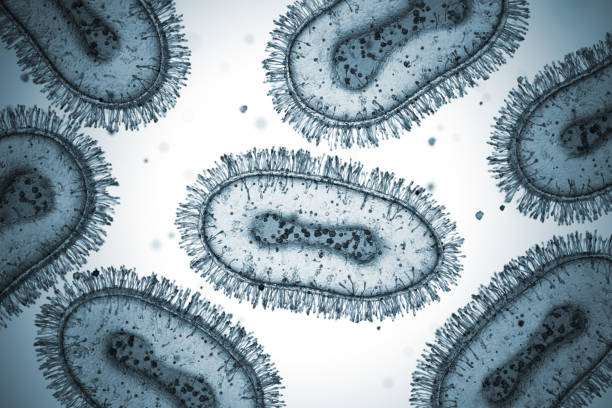
- Viruses: Although technically not living organisms, viruses are often studied under the microscope due to their importance in biology and medicine. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and can only be observed using electron microscopes.
Cell Structure:
All living things, whether visible or microscopic, are made of cells.
Cells have different structures, including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells).
Cell Types:
Cells can be classified into two main types: prokaryotic cells (as seen in bacteria) and eukaryotic cells (as seen in plants, animals, and some microscopic organisms).
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have these structures.
Cell Functions:
Cells have various functions, such as growth, reproduction, and responding to their environment.
Different types of cells have specialized functions in multicellular organisms, contributing to the overall health and functioning of the organism.
Microscope Use and Safety:
When using microscopes, it’s essential to follow safety guidelines, such as handling slides carefully and keeping the microscope clean.
Proper lighting, focusing, and adjusting the magnification are important for obtaining clear images.
Importance of Microscopy:
Microscopy is crucial in fields like biology, medicine, and microbiology for studying and diagnosing diseases, conducting research, and understanding the microscopic world.
Applications of Microscopy:
Microscopy is used in various scientific fields, including microbiology, genetics, and cell biology, to explore the structure and function of living things at the microscopic level.
Conclusion:
Learning about living things under the microscope is fascinating and provides insights into the hidden world of tiny organisms and cells that play essential roles in our environment and our bodies.
Let’s practice!

