Response to stimulus
Key Notes :
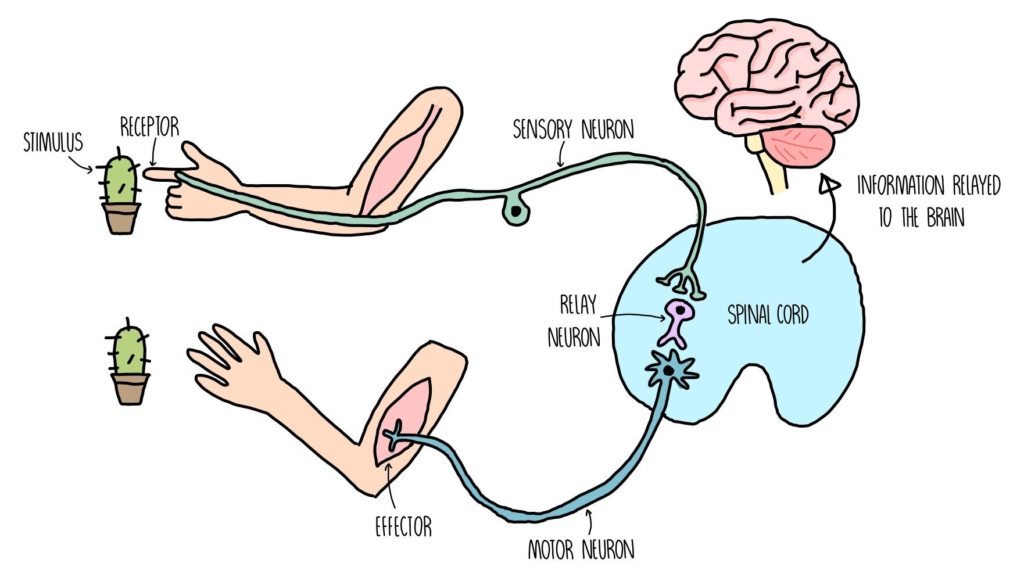
- What is a Stimulus?
- A stimulus is a signal or change in the environment that organisms detect through their senses. It can be internal (inside the body) or external (outside the body).
- Types of Stimuli:
- External stimuli: These come from the outside environment, such as light, sound, temperature, or touch.
- Internal stimuli: These originate within an organism, like hunger, pain, or thirst.
- Sensory Organs:
- Living organisms have specialized sensory organs to detect different types of stimuli. For example, eyes detect light, ears detect sound, and skin detects touch.
- Response to Stimulus:
- Organisms respond to stimuli to survive and adapt to their environment.
- A response can be a physical or behavioral change. For instance, moving away from a painful stimulus like a hot object.
- Nervous System:
- Many animals have a nervous system that plays a crucial role in detecting and responding to stimuli. It includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Reflexes:
- Reflexes are rapid, involuntary responses to a stimulus. They help protect the body from harm without conscious thought. For example, the knee-jerk reflex when a doctor taps your knee with a hammer.
- Types of Responses:
- Positive response: An organism moves towards a stimulus that benefits it, like reaching for food when hungry.
- Negative response: An organism moves away from a stimulus that harms it, like running from a predator.
- Adaptations:
- Over time, organisms can adapt to their environment by developing responses to specific stimuli. This is a key aspect of evolution.
- Tropism:
- Plants also respond to stimuli through a process called tropism. For example, phototropism is when a plant grows towards light.
- Instinct and Learning:
- Some responses are instinctual, meaning they are hardwired into an organism’s genetics. Others are learned through experience.
- Habituation and Sensitization:
- Habituation is when an organism becomes less responsive to a repeated stimulus that has no negative or positive consequences.
- Sensitization is the opposite, where an organism becomes more responsive to a repeated or intensified stimulus.
- In summary:
- Organisms respond to stimuli through specialized sensory organs and their nervous systems.
- Responses can be voluntary or involuntary, and they help organisms survive and adapt to their surroundings.
Let’s practice!

