Rainwater Harvesting
Key Notes :
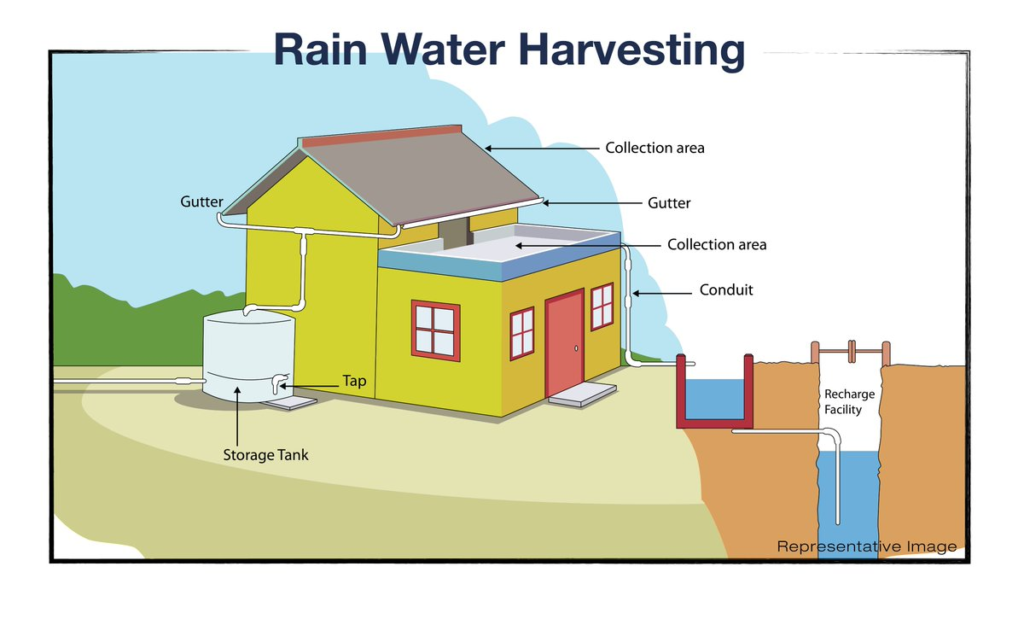
Definition:
- Rainwater Harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use. It is an eco-friendly method to conserve water, especially in areas with limited water resources.
Importance:
- Conserves water: Helps in saving water for drinking, irrigation, and other daily needs.
- Reduces Water Shortage: Provides an alternative source of water during dry seasons.
- Prevents Flooding: By collecting rainwater, it prevents excessive runoff and flooding.
- Reduces Dependency on Groundwater: Helps in reducing the use of groundwater, which may deplete over time.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting:
- Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting: Water is collected from roofs and stored in tanks or wells.
- Surface Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater from roads, fields, or other surfaces, and storing it in ponds or reservoirs.
- Infiltration Wells: Water is directed into wells or underground tanks where it can recharge groundwater levels.
Steps Involved:
- Collection: Water is collected from rooftops or other surfaces using gutters and pipes.
- Storage: Collected water is stored in tanks or underground reservoirs.
- Filtration: Filtration methods are used to remove impurities and ensure the water is safe for use.
Uses of Collected Rainwater:
- Drinking: After proper treatment and filtration.
- Irrigation: Used for watering crops and gardens.
- Domestic Use: Washing, cleaning, and flushing toilets.
- Groundwater Recharge: Replenishes underground water sources.
Benefits:
- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces the impact on the environment by using a renewable resource.
- Cost-effective: Reduces water bills for households and institutions.
- Prevents Soil Erosion: Reduces water runoff that can cause soil erosion.
Challenges:
- Initial Setup Cost: Installing rainwater harvesting systems can be expensive.
- Maintenance: The system needs to be maintained regularly to ensure water quality.
- Weather Dependency: Water availability depends on rainfall patterns.
Simple Rainwater Harvesting System (for students):
- Gutter system to collect water from the roof.
- Filter to remove debris.
- Storage tank to store the clean water.
- Overflow system to prevent overflow and flooding.
Real-life Examples:
- Schools and Homes: Many schools and homes have rainwater harvesting systems to conserve water.
- Cities: Some cities have adopted large-scale rainwater harvesting systems to cope with water scarcity.
Let’s practice!

