What Do Animals Eat
Key Notes :
Types of Animal Diets:
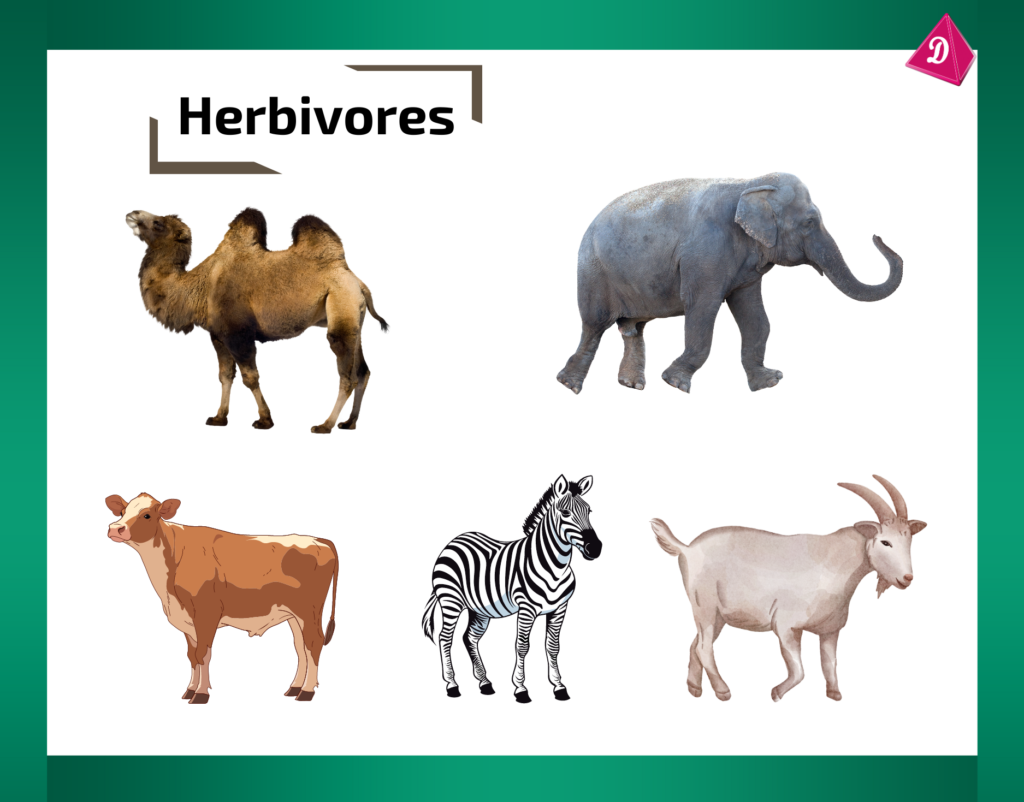
- Herbivores: Animals that eat plants. Examples include cows, deer, and elephants. They have specialized teeth for grinding leaves and grasses.

- Carnivores: Animals that eat other animals. Examples include lions, tigers, and eagles. They have sharp teeth and claws for catching and tearing meat.

- Omnivores: Animals that eat both plants and animals. Examples include bears, humans, and pigs. They have a combination of sharp and flat teeth to handle a variety of foods.

Food Chains and Food Webs:
- Food Chain: A sequence that shows how energy and nutrients flow from one organism to another. For example, grass → rabbit → fox.

- Food Web: A complex network of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem, showing how different animals are related through their food sources.

Feeding Adaptations:
- Beaks and Teeth: Different shapes and sizes adapted for specific diets, such as the long beak of a hummingbird for nectar or the strong jaws of a crocodile for meat.

- Digestive Systems: Vary among animals to process their specific diets. Ruminants like cows have a complex stomach to digest tough plant material, while carnivores have a simpler digestive tract for meat.
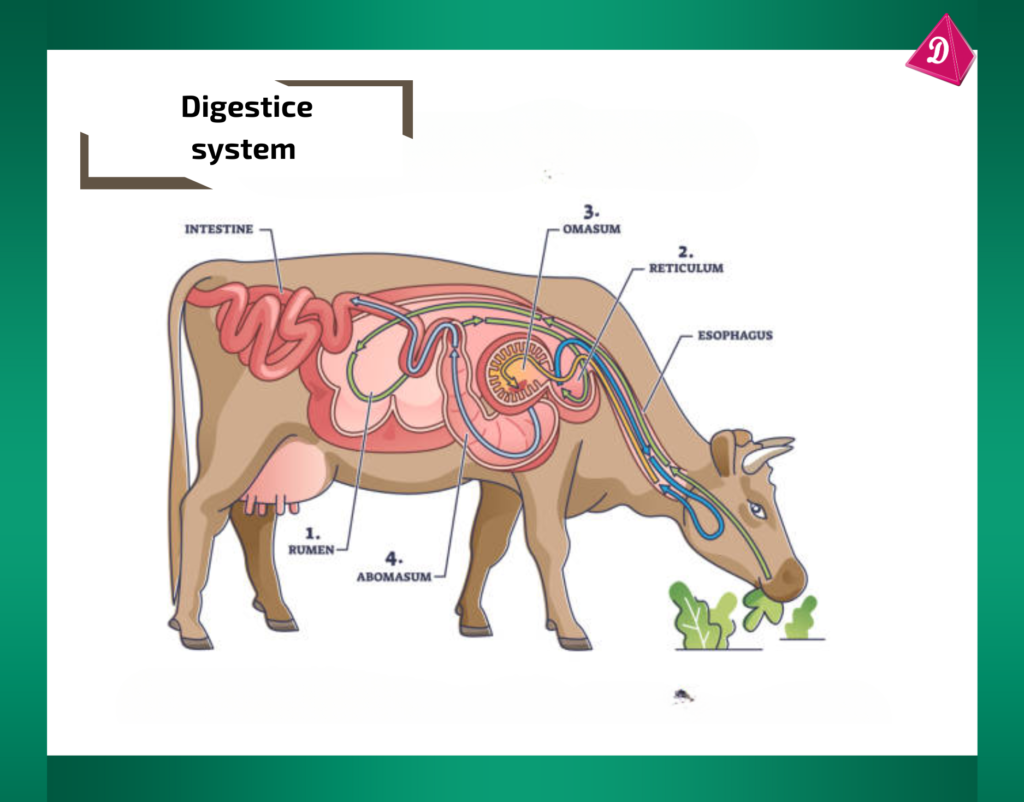
Specialized Diets:
- Insectivores: Animals that primarily eat insects, such as anteaters and frogs.

- Frugivores: Animals that mainly consume fruits, like many birds and some bats.

- Nectarivores: Animals that feed on nectar, such as hummingbirds and certain butterflies.

Aquatic Animal Diets:
- Plankton Eaters: Many marine animals like whales and small fish consume plankton, tiny organisms drifting in the water.
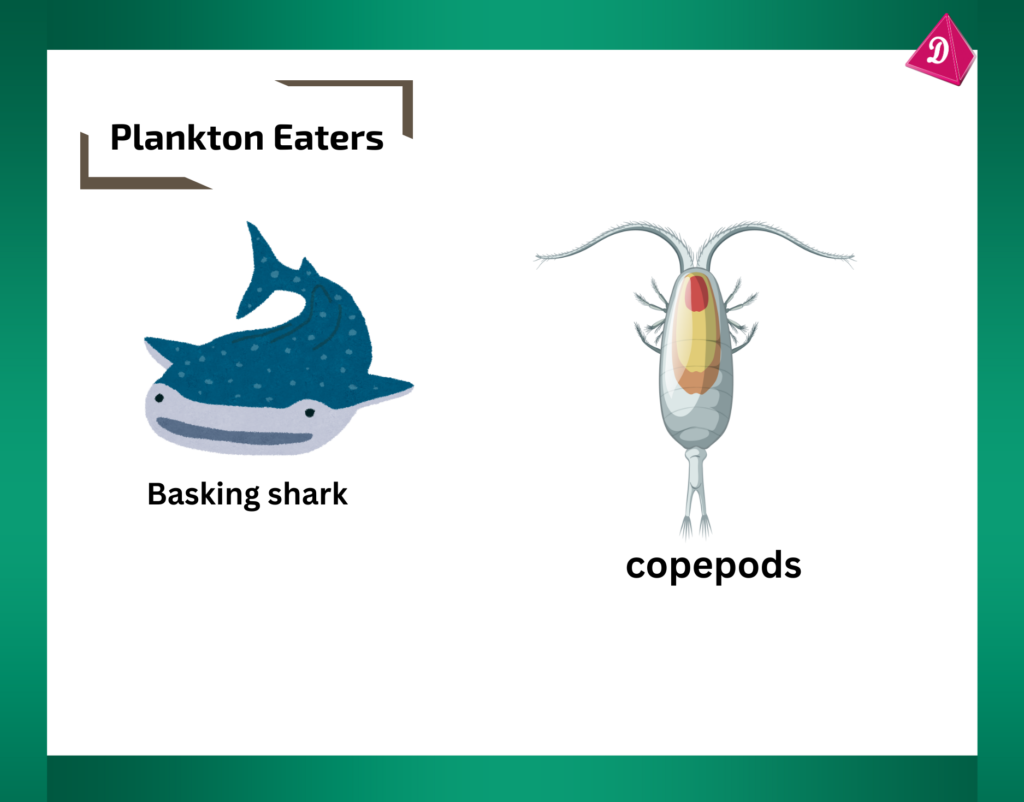
- Predatory Fish: Larger fish like sharks and tuna eat other fish and marine animals.

Scavengers and Decomposers:
- Scavengers: Animals that consume dead animals, playing a crucial role in cleaning the environment. Examples include vultures and hyenas.

- Decomposers: Organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
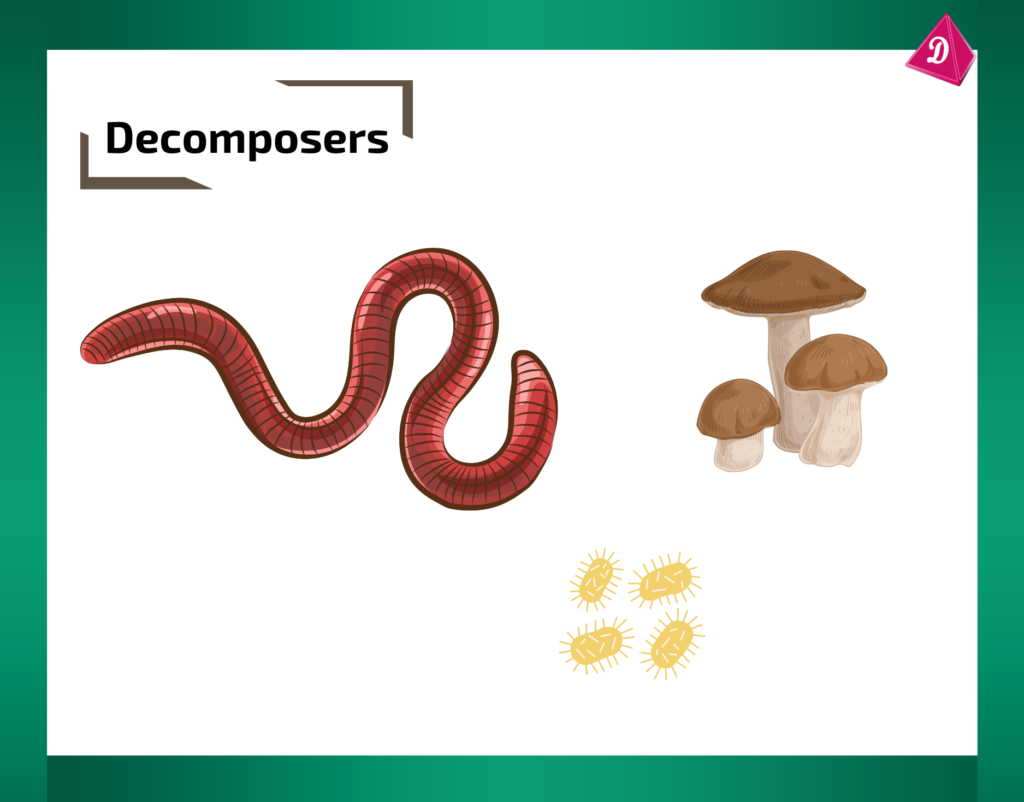
Human Impact on Animal Diets:

- Habitat Destruction: Reduces the availability of natural food sources for many animals.
- Pollution: Contaminates food sources, affecting animal health.
- Climate Change: Alters habitats and food availability, forcing animals to adapt or migrate.
Let’s practice!

