Integers on number lines
key notes:
Definition of Integers:
- Integers include all whole numbers, both positive and negative, as well as zero. Examples: -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3.
Understanding the Number Line:
- A number line is a straight line that represents numbers at equal intervals. It extends infinitely in both directions.
- The center point is zero (0), with positive integers to the right and negative integers to the left.
Positive and Negative Integers:
- Positive integers are found to the right of zero and are greater than zero.
- Negative integers are found to the left of zero and are less than zero.
Zero on the Number Line:
- Zero is a unique integer that separates positive and negative integers. It is neither positive nor negative.
Plotting Integers:
- To plot an integer on a number line, identify its position based on its value:
- Example: To plot -2, move two spaces to the left of zero. To plot 3, move three spaces to the right of zero.
Comparing Integers:
- When comparing integers, the further right on the number line, the larger the number. For example, -1 is greater than -2 because -1 is to the right of -2 on the number line.
Learn with an example
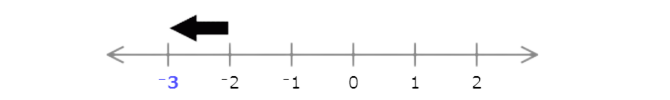
Type the missing number.

Each interval represents 1, so find the missing number by adding or subtracting 1.
The missing number is smaller than –5, so subtract 1. Since –5 − 1 = –6, the missing number is –6.
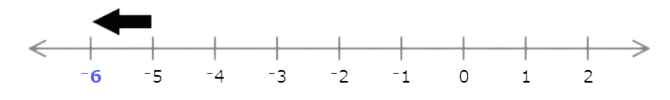
Type the missing number.

Each interval represents 1, so find the missing number by adding or subtracting 1.
The missing number is larger than 0, so add 1. Since 0 + 1 = 1, the missing number is 1.
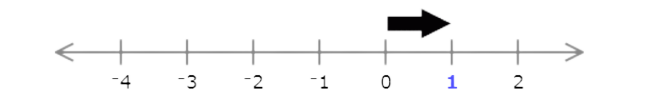
Type the missing number.

Each interval represents 1, so find the missing number by adding or subtracting 1.
The missing number is smaller than –2, so subtract 1. Since –2 − 1 = –3, the missing number is –3.