Fractions and mixed numbers
key notes:
1. Understanding Fractions
- A fraction represents a part of a whole and is written in the form a/b, where:
- Numerator (top number) shows how many parts are being considered.
- Denominator (bottom number) shows the total number of equal parts.
- Types of Fractions:
- Proper Fraction: Numerator is less than the denominator (e.g., 3/4).
- Improper Fraction: Numerator is equal to or greater than the denominator (e.g., 5/3).
- Equivalent Fractions: Fractions that have different numerators and denominators but represent the same value (e.g., 1/2 and 2/4).
2. Mixed Numbers
- A mixed number has a whole number and a proper fraction combined (e.g., 2 (1/3)).
- Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator.
- Write the quotient as the whole number and the remainder as the numerator of the fraction.
- Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
- Add the numerator to this product and place it over the original denominator.
3. Adding and Subtracting Fractions
- Same Denominators: Add or subtract the numerators and keep the denominator.
- Different Denominators:
- Find a common denominator by finding the least common multiple (LCM).
- Convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with this common denominator.
- Add or subtract the numerators and simplify if needed.
4. Multiplying Fractions
- Multiply the numerators and the denominators directly.
- Simplify the result if possible by dividing both numerator and denominator by their greatest common factor (GCF).
5. Dividing Fractions
- To divide fractions, multiply by the reciprocal (flip the second fraction).
- Simplify the result if needed.
6. Comparing and Ordering Fractions
- Use a common denominator to compare fractions.
- For ordering, convert fractions to have the same denominator and arrange from smallest to largest (or vice versa).
7. Simplifying Fractions
- A fraction is simplified when the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1.
- Divide both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF to simplify.
8. Applications of Fractions and Mixed Numbers
- Fractions and mixed numbers are used in daily life for tasks like cooking (measuring ingredients), dividing items, and managing portions.
Learn with an example
What fraction of the shapes are triangles?
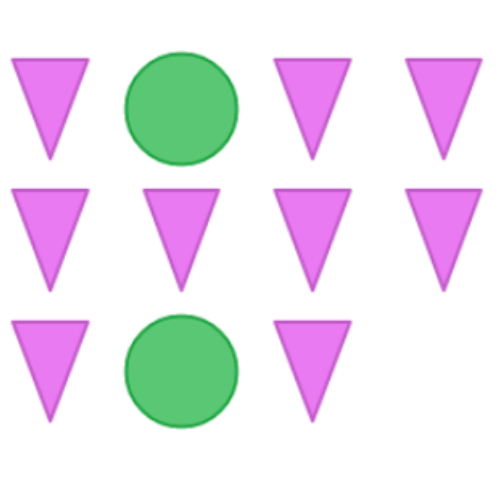
Use a forward slash ( / ) to separate the numerator and denominator.
Count the number of shapes. There are 11 shapes.
Count the number of triangles. There are 9 triangles.
9 out of 11 shapes are triangles. Write 9 out of 11 as a fraction:
9/11
What fraction does the number line show?

Use a forward slash ( / ) to separate the numerator and denominator.
Count the number of segments between 0 and 1. There are 7 segments.
Now count the number of segments between 0 and the dot. There are 4 segments.
The number line shows 4/7 .
What fraction of the shapes are triangles?

Count the number of shapes. There are 11 shapes.
Count the number of triangles. There are 4 triangles.
4 out of 11 shapes are triangles. Write 4 out of 11 as a fraction:
4/11

Let’s practice!

