Decimal number lines
key notes:
| Understanding Decimal Numbers: |
Decimal numbers are numbers that have a whole number part and a fractional part, separated by a decimal point (e.g., 3.5, 0.75).
The digits after the decimal point represent parts of a whole, with the place value decreasing by powers of 10 (tenths, hundredths, thousandths).
| Decimal Number Line: |
A decimal number line is a number line that includes both whole numbers and decimal values.
It helps visualize the position of decimal numbers relative to whole numbers and other decimals.
| Placing Decimals on a Number Line: |
Start by drawing a number line with whole numbers at equal intervals.
Divide the space between two whole numbers into equal parts (tenths, hundredths, etc.), depending on the decimal’s place value.
For example, to plot 2.3, divide the space between 2 and 3 into 10 equal parts and count three parts over from 2.
| Reading and Interpreting Decimals on a Number Line: |
The position of a decimal on the number line corresponds to its value.
Decimals are placed based on their value relative to the whole numbers on the number line.
For example, 1.4 is placed closer to 1 than to 2, since it is slightly more than 1 but less than 2.
| Adding and Subtracting Decimals Using a Number Line: |
To add decimals, move to the right on the number line.
To subtract decimals, move to the left on the number line.
The number of steps you move depends on the decimal place value.
| Comparing Decimals Using a Number Line: |
Decimals with larger values are placed farther to the right on the number line.
Decimals with smaller values are placed farther to the left.
By comparing their positions on the number line, you can determine which decimal is greater or smaller.
| Examples: |
Plotting 0.6 on the number line: Divide the space between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts. The sixth mark represents 0.6.
Plotting 2.75 on the number line: Divide the space between 2 and 3 into 100 equal parts (for hundredths). Count 75 parts over from 2 to get 2.75.
| Decimal Place Value on a Number Line: |
Tenths: The first place to the right of the decimal point (e.g., 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, etc.).
Hundredths: The second place to the right of the decimal point (e.g., 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, etc.).
Thousandths: The third place to the right of the decimal point (e.g., 0.001, 0.002, etc.).
| Importance of Decimal Number Lines: |
Decimal number lines help students visually understand the relationship between decimals and whole numbers.
They enhance the ability to compare and order decimal numbers.
Decimal number lines are useful for adding, subtracting, and estimating decimal numbers.
Learn with an example
🔔 Find the value of r.
Write your answer as a decimal number.
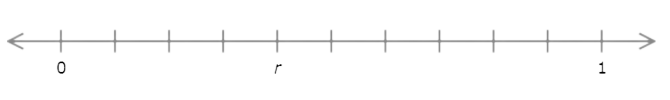
r =
The number line goes from 0 to 1 with ten equal intervals. Each interval represents 0.1.
Count the intervals from 0 to r. There are 4 intervals. r is 0.4 greater than 0.
r = 0.4
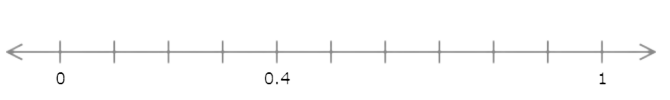
🔔 Find the value of d.
Write your answer as a decimal number.
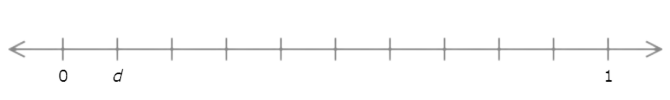
d =
The number line goes from 0 to 1 with ten equal intervals. Each interval represents 0.1.
Count the intervals from 0 to d. There is 1 interval. d is 0.1 greater than 0.
d = 0.1
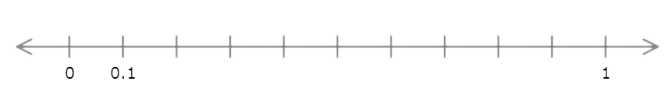
Find the value of t.
Write your answer as a decimal number.
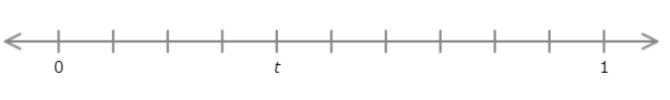
t = ______
The number line goes from 0 to 1 with ten equal intervals. Each interval represents 0.1.
Count the intervals from 0 to t. There are 4 intervals. t is 0.4 greater than 0.
t = 0.4
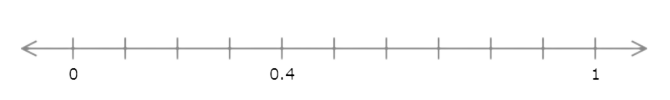
let’s practice:

