What decimal number is illustrated?
key notes:
| Understanding Decimals |
- A decimal number is a way to represent fractions and whole numbers together using a decimal point.
- The position of each digit in a decimal number indicates its value (place value).
| Place Value in Decimals |
Digits to the left of the decimal point represent whole numbers (e.g., ones, tens, hundreds).
Digits to the right of the decimal point represent fractional parts:
- Tenths (1/10): First place after the decimal.
- Hundredths (1/100): Second place after the decimal.
- Thousandths (1/1000): Third place after the decimal.
| Visualizing Decimals |
Grids:
- A 10×10 grid represents 1 unit divided into 100 equal parts (hundredths).
- Example: If 45 squares are shaded, the decimal is 0.45 (45/100).
Number Lines:
- Decimals are placed between whole numbers.
- Example: On a number line from 0 to 1, the point halfway represents 0.5.
| Interpreting Decimal Representations |
Shaded Figures: Count the shaded parts and divide by the total parts to determine the decimal.
- Example: In a circle divided into 10 equal parts with 7 shaded, the decimal is 0.7.
Bar Models: Identify the fraction of the bar shaded and convert it to a decimal.
- Example: A bar divided into 5 parts with 3 shaded represents 0.6 (3/5 = 0.6).
| Converting Decimals to Fractions |
Write the decimal as a fraction and simplify if needed.
- Example: 0.75 = 75/100 = 3/4.
| Common Decimal Equivalents |
- 1/2 = 0.5
- 1/4 = 0.25
- 3/4 = 0.75
- 1/10 = 0.1
| Real-Life Applications |
Understanding decimals is essential for money calculations, measurements, and data interpretation.
| Activities to Practice |
- Identify the decimal represented by shaded parts of a grid or figure.
- Place decimal numbers correctly on a number line.
- Convert fractions from visual representations into decimals.
| Examples: |
- Grid Example:
A grid with 100 squares has 62 shaded. The decimal is 0.62. - Number Line Example:
A point halfway between 1 and 2 on a number line is 1.5. - Shaded Circle Example:
A circle divided into 10 parts with 3 shaded is 0.3.
Learn with an example
What decimal number is illustrated?
There are 100 squares. There are 22 colored squares. This picture shows twenty-two hundredths.
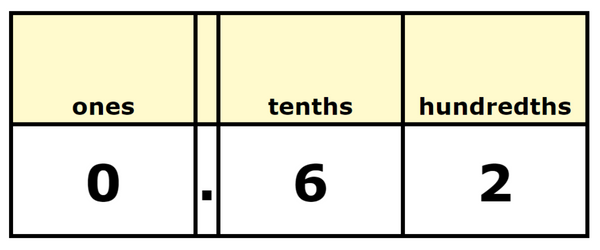
Now write twenty-two hundredths as a decimal. Use a place value chart.
| ones | tenths | hundredths | |
| 0 | . | 2 | 2 |
The answer is 0.22.
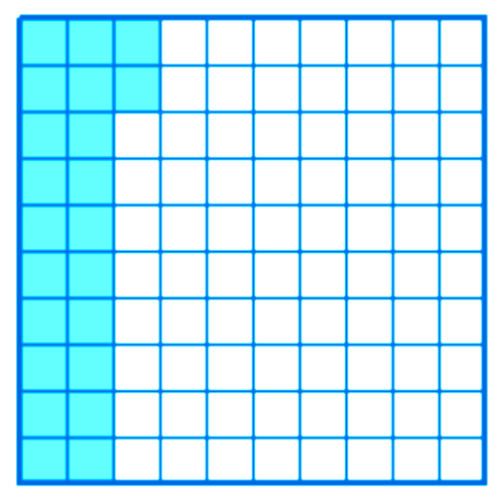
What decimal number is illustrated?

There are 100 squares. There are 62 colored squares. This picture shows sixty-two hundredths.
Now write sixty-two hundredths as a decimal. Use a place value chart.
The answer is 0.62.
What decimal number is illustrated?
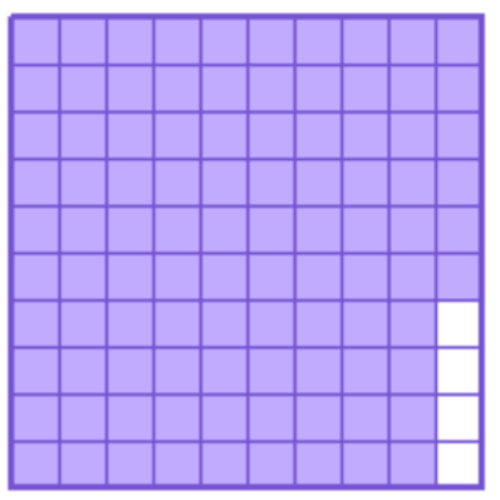
There are 100 squares. There are 96 coloured squares. This picture shows ninety-six hundredths.
Now write ninety-six hundredths as a decimal. Use a place value chart.

The answer is 0.96.

let’s practice:

